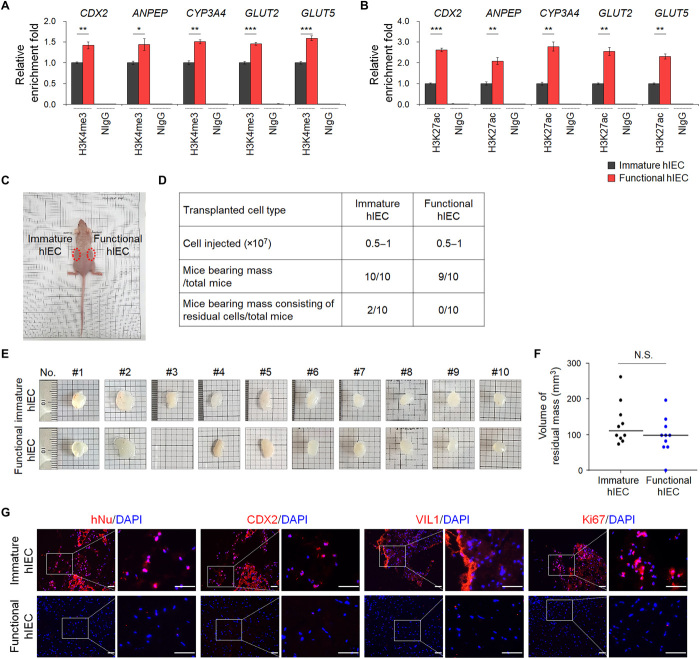
Fig. 4. The epigenetic status and in vivo cell retention capacity of functional hIECs.
The ChIP assay was performed using anti-H3K4me3 (A) and anti-H3K27ac antibodies (B). The result is shown as a relative enrichment fold compared to immature hIECs using a percentage of the input chromatin, n = 3. NIgG, normal IgG. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed t test. (C) Nude mice were injected subcutaneously with immature (left side) or functional hIECs (right side) on both sides, and each plug contained 0.5 to 1 × 107 cells within the Matrigel. (D) A summary of cell retention capacity of immature or functional hIECs. (E) Representative images of hIEC-Matrigel plugs recovered from mice after 6 to 10 weeks. (F) hIEC-Matrigel plugs were isolated 6 to 10 weeks after transplantation and volumes were measured. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 10). N.S. indicates nonsignificant by two-tailed t test. (G) Immunofluorescence analysis for human nuclei (hNu), intestinal markers (CDX2 and VIL1), and proliferation marker (Ki67) in hIEC-Matrigel plugs. Scale bars, 50 μm.