Figure 7.
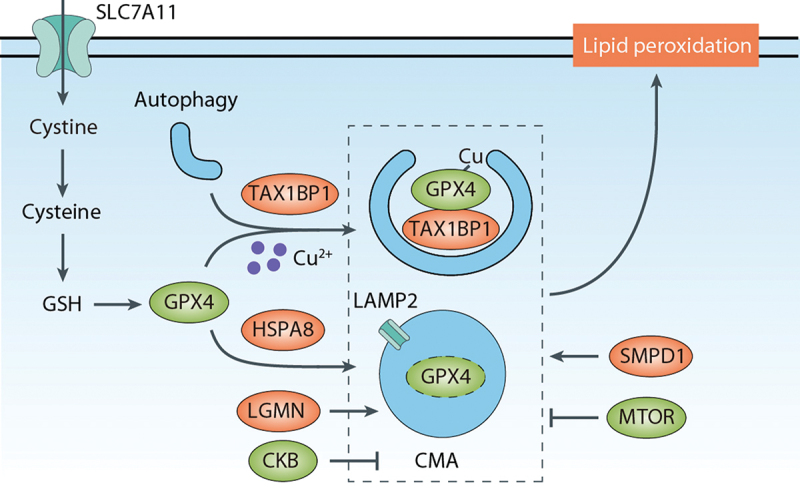
CMA- or TAX1BP1-mediated GPX4 degradation in ferroptosis. CMA serves as a pathway for GPX4 protein degradation during ferroptosis. LAMP2 plays a key role in transporting GPX4 across the lysosomal membrane, and HSPA8/HSC70 interacts with GPX4 and LAMP2, facilitating CMA. CMA-mediated degradation of GPX4 can be inhibited by CKB-mediated GPX4 phosphorylation. LGMN assists in CMA-mediated GPX4 degradation. Furthermore, macroautophagy/autophagy also contributes to GPX4 degradation during ferroptosis. SMPD1/ASM promotes the autophagic degradation of GPX4, whereas MTOR inhibits GPX4 protein degradation and subsequent ferroptosis. Copper directly binds to GPX4, leading to its autophagic degradation, and, in this process, TAX1BP1 acts as an autophagic receptor.
