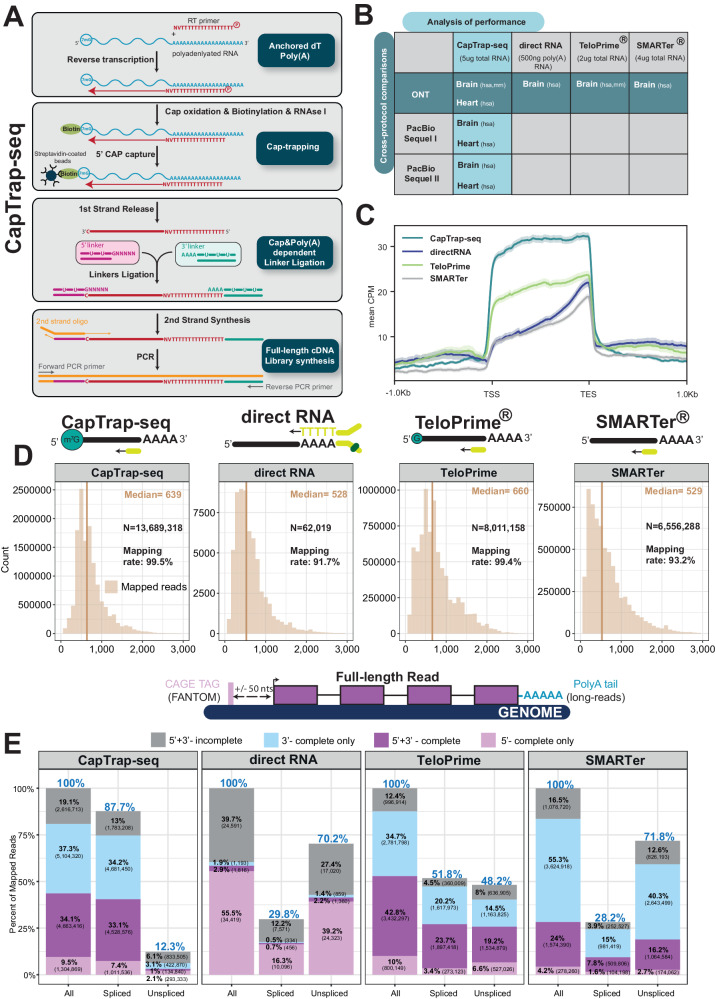
Fig. 1. Full-length transcript annotation using CapTrap-seq and other library preparation methods.
A CapTrap-seq experimental workflow. Gray boxes highlight the four main steps of full-length (FL) cDNA library construction: Anchored dT Poly(A)+, CAP-trapping23–26, CAP and Poly(A) dependent linker ligation, and FL-cDNA library enrichment as described in the text. B Two adult human complex transcriptomic samples, brain and heart, were used to perform the cross-protocol and cross-platform comparisons to assess the quality of CapTrap-seq. The horizontal green line indicates the cross-protocol comparisons, including four different sequencing library preparation methods: CapTrap-seq, directRNA®, TeloPrime®, and SMARTer®. Whereas, the vertical blue line shows cross-platform comparison using CapTrap-seq in combination with three long-read sequencing platforms: ONT, PacBio Sequel I, and Sequel II. C Read aggregate deepTools251 profiles along the body of annotated GENCODE genes. The shaded regions indicate the 95% confidence interval. D Length distribution of mapped long-read ONT reads for each protocol. The total number of reads (N), median read length (beige vertical line), and the mapping rate are shown in the top right corner. E Detection of full-length reads among all, spliced and unspliced reads, with 5′ and 3′ termini inferred from robust (FANTOM5 phase 1 and 2 robust (n = 201,802)) CAGE clusters33 and poly(A) tails. Colors highlights four different categories of long-read (LR) completeness: Gray: unsupported LRs; Sky blue: 3’ supported LRs; Light pink: 5’ supported LRs; Purple: 5’ + 3’ supported LRs. The blue percentage displayed at the top of each bar indicates the ratio of a specific read type (spliced, unspliced) to the total number of reads.