FIGURE 4.
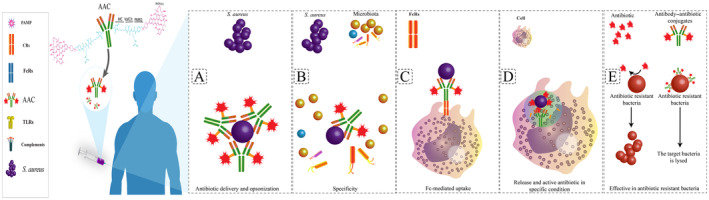
Advantages and overall structure of antibody–antibiotic conjugates (AAC). (A) Antibiotic delivery and opsonization: AACs enable precise delivery of antibiotics to target bacteria, ensuring efficient opsonization for enhanced phagocytosis. (B) Specificity: AACs exhibit high specificity by targeting surface antigens on bacteria, minimizing off‐target effects on host cells. (C) Fc‐mediated uptake: AACs utilize Fc receptors (FcR) to facilitate uptake by immune cells, enhancing the clearance of intracellular bacteria. (D) Release and active antibiotic in specific conditions: Within intracellular environments like phagolysosomes, AACs release active antibiotics, ensuring effective bacterial eradication. (E) Effective in antibiotic‐resistant bacteria: AACs demonstrate efficacy even against antibiotic‐resistant bacterial strains, addressing the challenge of antibiotic resistance.
