Figure 4.
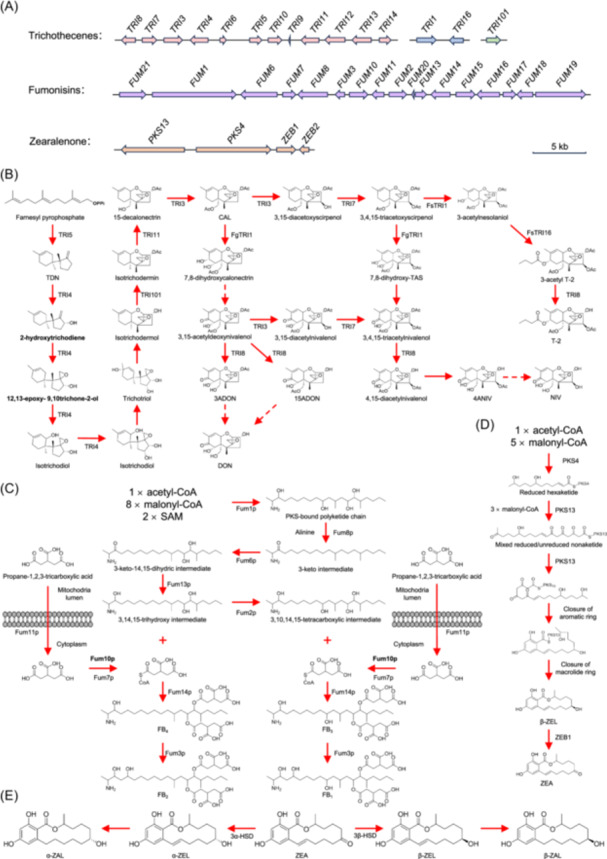
The formation approaches of Fusarium mycotoxins. (A) Mycotoxin biosynthetic genes and gene clusters in Fusarium. Arrows denote the location and transcriptional orientation of genes, while the corresponding gene name is provided adjacent to each arrow. (B) The proposed pathway of TRI biosynthesis. The 3,4,15‐triacetoxyscirpenol is an important branching point. One path leads to a Type A TRI, and the other leads to a Type B TRI. In F. sporotrichioides, FsRI1 exclusively catalyzes hydroxylation of 3,4,15‐triacetoxyscirpenol at C‐8, resulting in Type A TRIs, while in F. graminearum, FgTRI1 mediates hydroxylation of 3,4,15‐triacetoxyscirpenol at both C‐7 and C‐8, resulting in Type B TRIs. Dashed arrows denote steps where gene assignment has not been established. (C) The proposed pathway of FUM biosynthesis. Fum11p, a tricarboxylate transporter, transports tricarboxylic acid precursors out of the inner mitochondrial lumen for FUM biosynthesis, while Fum7p and Fum10p catalyze the conversion of tricarboxylic acid precursors into acetyl CoA‐activated tricarballylic acid. This product is then esterified to the polyketide backbone at C‐14 and C‐15 by Fum14p to produce either FB3 or FB4. Finally, the hydroxylation of FB3 and FB4 by Fum3p yields FB1 and FB2, respectively. (D) The proposed pathway of ZEA biosynthesis. The biosynthesis begins with PKS4, which facilitates the condensation of carbons derived from one acetyl‐CoA and five malonyl‐CoAs. PKS13 completes the polyketide backbone as an extender unit and is responsible for cyclization and aromatization. As the final step, β‐ZEL is converted into ZEA by ZEB1. (E) The formation pattern of metabolites of ZEA. The C6 keto group of ZEA is reduced to yield α‐ZEL and β‐ZEL, followed by a subsequent reduction at the C11–C12 double bond that results in the formation of α‐ZAL and β‐ZAL, respectively. Those proposed biosynthesis and metabolites pathways were derived from the works of McCormick et al. 17 , Alexander et al 21 , Nahle et al 23 and EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM) et al 74 . CAL, calonectrin; FgTRI1, F. graminearum TRI1; FsTRI1, F. sporotrichioides TRI1; FUM, fumonisin; PKS, polyketide synthase; SAM, S‐adenosyl methionine; TRI, trichothecenes; ZEA, zearalenone.
