Figure 5.
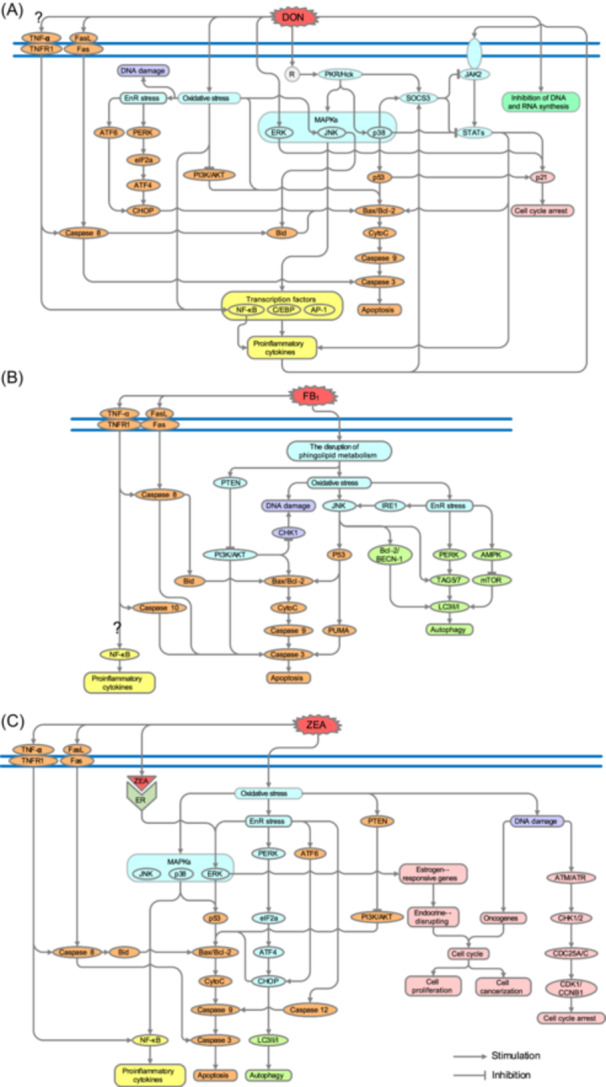
The toxicological mechanisms of the main Fusarium mycotoxins. (A) DON‐induced oxidative stress can cause DNA damage, EnR stress, and the suppression of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Consequently, it can lead to a decrease in Bcl‐2 gene expression, an increase in Bax gene expression, and elevated levels of CytoC expression. It enhances the upregulated expression of Caspase 9 and Caspase 3 and induces apoptosis. DON can efficiently induce the activation of MAPKs through a mechanism referred to as the “ribotoxic stress response” and hijack the JAK2/STAT‐3 pathway to induce apoptosis, proinflammatory cytokine upregulation, and cell cycle arrest. DON also activates Caspase 8 to increase expression of Caspase 3 by the tumor necrosis factor‐α and Fas/FasL signaling pathways, leading to apoptosis. (B) FB1 disrupts sphingolipid metabolism, causing DNA damage and apoptosis through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as well as oxidative stress, which further entrenches DNA damage and apoptosis and induces EnR stress. FB1‐induced EnR stress not only causes apoptosis by the JNK/p53/PUMA/Caspase 3 pathway but also leads to autophagy via signaling pathways mediated by IRE1, PERK, and AMPK. IRE1 can activate JNK, which results in the subsequent elevation of BECN1, ATG5, and ATG7 and the conversion of LC3‐I. PERK induces the expression of ATG5 and ATG7 to form the ATG5–ATG7 complex and promotes the conversion of LC3‐I into LC3‐II. Under EnR stress, AMPK inhibits the anabolic process of mTOR, thereby increasing the expression of autophagy‐related genes and triggering autophagy. (C) ZEA and its derivatives can bind to ERs to elicit estrogen‐like effects and promote cellular proliferation. ZEA‐induced DNA damage can upregulate ATM and ATR expression and activate DNA damage checkpoints CHK1 and CHK2 to repair DNA damage. Next, the expression levels of CDC25A and CDC25C are upregulated, which promotes the expression of CCNB1 and CDK1, thus preventing the cell cycle from exiting the G2/M phase. Moreover, ZEA can induce apoptosis and autophagy similar to FB1 and DON. Question marks indicate indeterminate roles. EnR, endoplasmic reticulum; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase.
