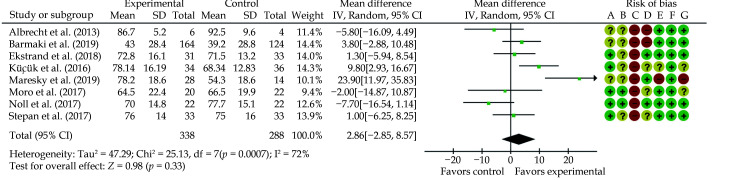
Figure 17.
Mean difference between groups in knowledge scores (using percentages).
(A): Random sequence generation (selection bias); (B): allocation concealment (selection bias); (C): blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias); (D): blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias); (E): incomplete outcome data (attrition bias); (F): selective reporting (reporting bias); and (G): other bias. Green colour indicates low risk of bias; yellow indicates unclear risk of bias; and red colour indicates high risk of bias. Reprinted with permission from Moro, et al.[114] “Control” indicates traditional teaching methods approaches; “Experimental” indicates augmented or virtual reality approaches.