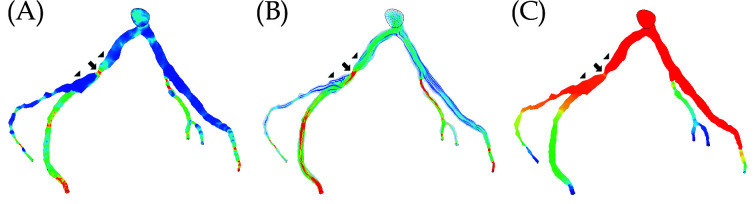
Figure 26.
Correlation between wider angulation and hemodynamic changes by CCTA-derived CFD analysis.
Left coronary bifurcation angle was measured 105º between the two main arterial branches, LAD and LCx with significant stenosis (> 70%) at LCx on CCTA and invasive coronary angiography in a 58-year-old man. (A and B): CFD analysis shows increased wall shear stress and flow velocity at the stenotic site of LCx. (C): CFD analysis shows decreased wall pressure at the same location. Arrow refers to the stenotic region at LCx, while arrowheads point to the pre- and post-stenotic locations. CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CFD: computational fluid dynamic; LAD: left anterior descending; LCx: left circumflex. Reprinted with permission under the open access from Sun and Chaichana.[190]