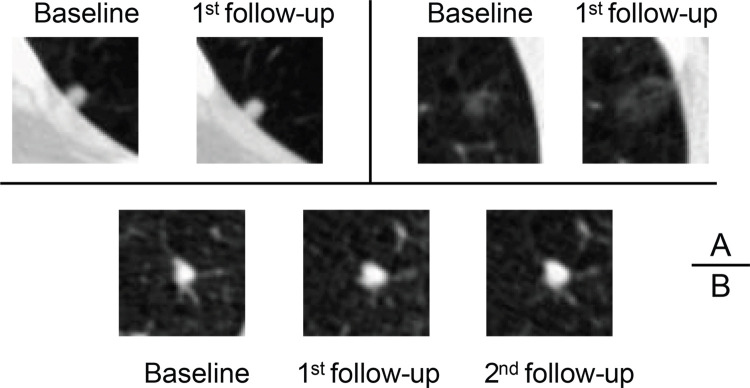
Figure 4:
Axial low-dose CT images show examples of small nodules (5 mm or less) without contrast media classified by the serial-year radiomics-based reinforcement learning (S-RRL) model and the Brock model at the baseline screening year. (A) Two malignant nodules were mistakenly classified as low risk by both models (false negatives). (B) The Brock model correctly classified this nodule as low risk. It was the only false-positive classification by the S-RRL model, likely because of the potential of nodule growth predicted by the S-RRL model which was confirmed at the follow-up scans.