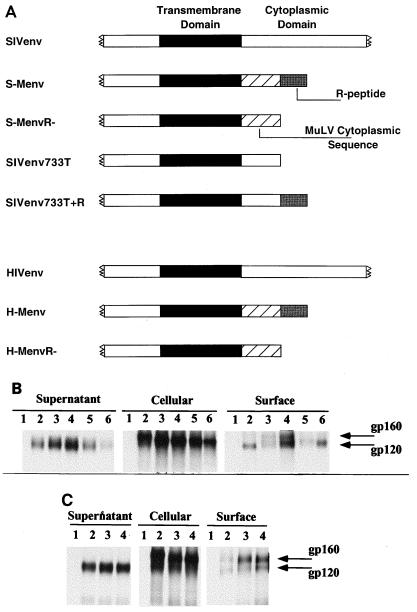
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic diagram of the transmembrane region of Env protein constructs used in this study. Black boxes represent the transmembrane domains of the SIV or HIV Env protein, hatched boxes represent cytoplasmic sequences of MuLV origin, gray boxes represent the MuLV R-peptide sequence, and white boxes represent the SU or cytoplasmic domain sequences of SIV or HIV origin (the SU and full-length cytoplasmic domains of SIV and HIV Env proteins are not drawn to scale). Construction of genes encoding the chimeric Env proteins was carried out by following standard cloning procedures described previously (42). (B) Expression of SIV and SIV-MuLV chimeric Env proteins. Lanes 1, mock transfection; lanes 2, full-length SIV Env; lanes 3, S-Menv; lanes 4, S-MenvR-; lanes 5, SIVenv733T+R; lanes 6, SIVenv733T. (C) Expression of HIV and HIV-MuLV chimeric Env proteins. Lanes 1, mock transfection; lanes 2, full-length HIV Env; lanes 3, H-Menv; lanes 4, H-MenvR-. Proteins were expressed in HeLa cells using the vaccinia virus T7 expression system (18). Surface biotinylation and immunoprecipitation were carried out as described previously (42).