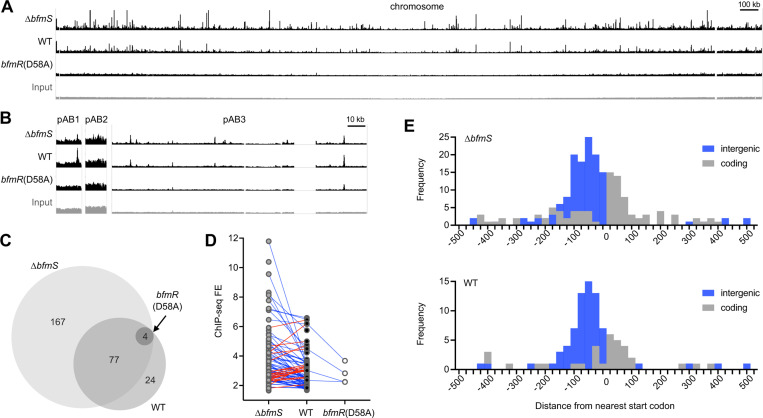
Fig. 5. BfmR binds to sites throughout the A. baumannii genome in a manner dependent on phosphorylation.
(A-B) Genome-wide BfmR binding sites revealed by ChIP-seq. Tracks show reads after ChIP-seq with the indicated strain, or input reads before ChIP from WT strain (input), mapped to the 17978 chromosome (A) or plasmids (B). Track height is 300 reads. Gap regions in chromosome and pAB3 read coverage correspond to unmapped endogenous transposon-related sequences. ΔbfmS refers to NRA49, WT refers to NRA28, and bfmR(D58A) refers to NRA29. (C) Venn diagram illustrating the number and relationships of BfmR binding sites detected in each strain. (D) Analysis of the relationship between FE for a binding site and strain background. Blue lines indicate sites in which FE was higher in ΔbfmS than WT. Red lines indicate sites in which FE was higher in WT vs ΔbfmS. (E) Histograms show the distance of the peak summit from the nearest ORF start codon. Binding sites in intergenic regions are shaded blue, and those within coding regions are shaded grey.