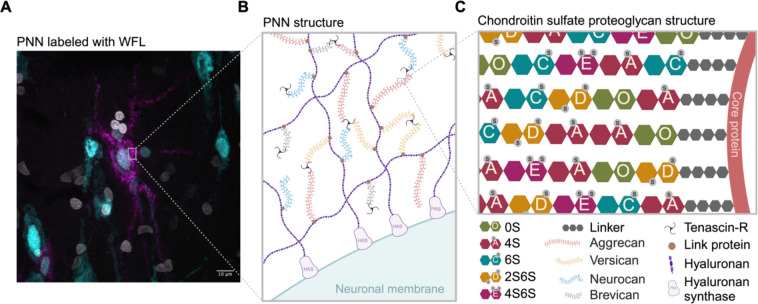
Fig. 1:
Perineuronal net composition and structure A Representative micrograph of a WFL+ PNN (magenta) surrounding the soma and proximal dendrites of a neuron (cyan) in the postmortem human entorhinal cortex. Nuclei (white). B PNNs are primarily composed of CSPGs from the lectican family (aggrecan, versican, neurocan and brevican) intricately linked to a hyaluronan backbone synthesized on the cell surface through link proteins. CSPGs are attached to each other through Tenascin-R, resulting in a distinctive net-like structure known as the PNN. C CSPGs have varying number of CS-GAG side chains made up of CS-disaccharides that exist in different isomers based on sulfate groups added to either C-4 or C-6 of the GalNAc or C-2 of GlcA including non-sulfated CS-O (0S), mono-sulfated CS-A (4S), -C (6S) and di-sulfated CS-D (2S6S), -E (4S6S). WFL: Wisteria Floribunda Lectin, PNN: perineuronal net, CSPGs: chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, CS-GAG: chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan, GalNAc: N-acetylgalactosamine, GlcA: D-glucuronic acid, HAS: hyaluronan synthase