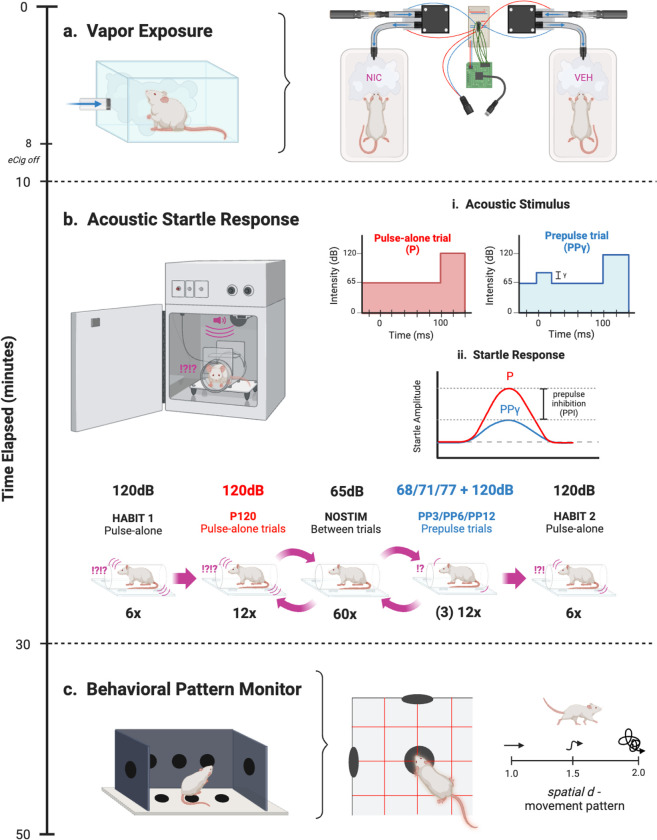
Fig. I. Experimental design.
a) Rats were exposed to VEH or NIC vapor in the OV system for 10 minutes. An Arduino microcontroller controlled two miniature vacuum pumps, each connected to an eCigarette input and mouse cage output via plastic tubing. b) Following a 5-minute acclamation in the startle chamber, either a high-intensity 120 dB acoustic stimulus alone (P) or high-intensity stimulus 120 dB preceded by a lower-intensity stimulus (PPγ) was presented against a constant 65 dB background, where γ is the varied prepulse stimulus intensity +3, +6, or +12 dB above background (volume of 68, 71, or 77 dB, respectively). Then, ASR was assessed following the stimulus to determine PPI, the difference in startle response between P and PPγ. Testing sessions were presented in 120 trials, with no stimulus trials spaced between P and PPγ trials. HABIT trials were used to assess startle reactivity. C) The BPM was used to assess animal movement and exploratory behavior through holes and infrared photobeams. In addition to activity (transitions and distance travelled) and exploratory measures (nose-poking and rearing), locomotor patterns were also quantified through spatial d. Spatial d values closer to 1 indicated more linear movement, while values closer to 2 indicated more sporadic movement