Fig. II. Nicotine eliminates intensity-dependent PPI deficits in HIV-1Tg rats.
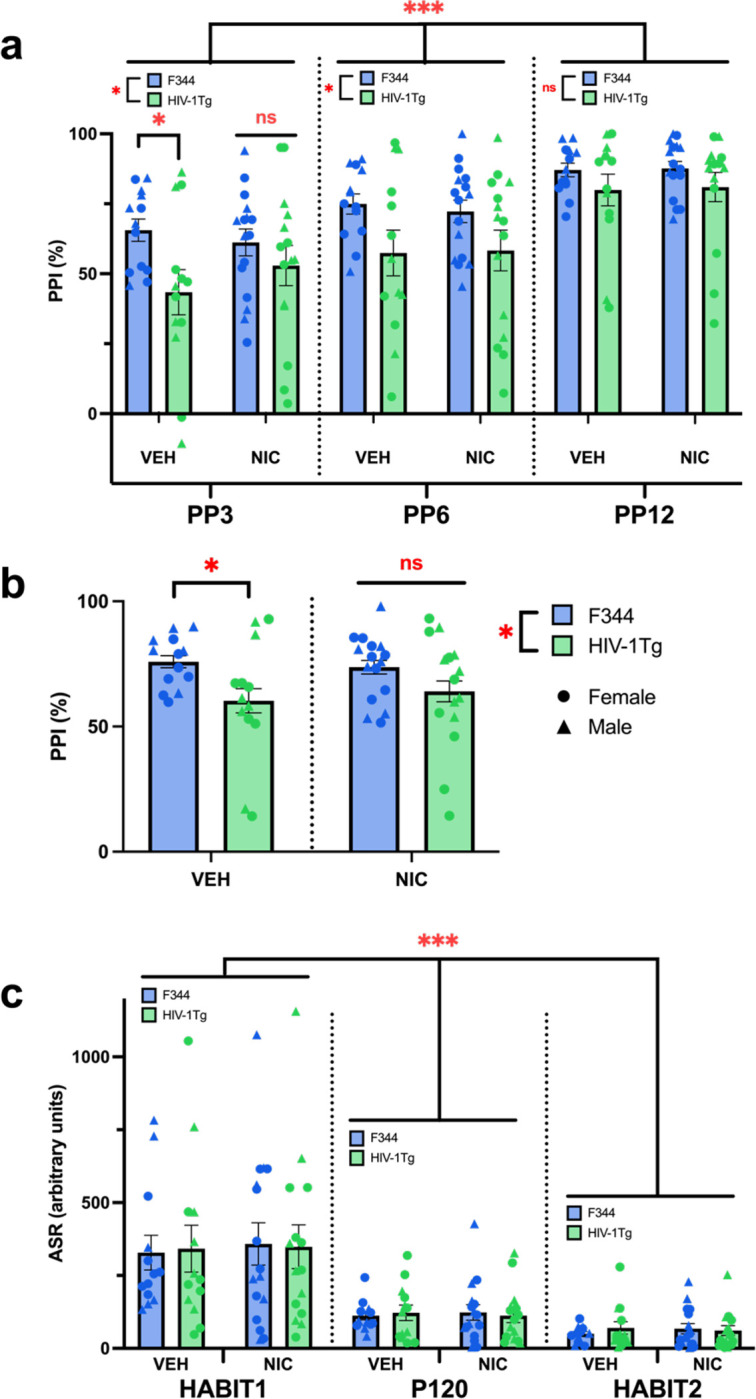
a) HIV-1Tgs had lower PPI than F344s at the lower prepulse intensities (PP3 and PP6), but not the highest (PP12). Planned comparisons at the PP3 level revealed that NIC normalized these deficits in HIV-1Tg rats. Within-subjects, louder prepulse intensities (PP3<PP6<PP12) elicited greater PPI. b) NIC also normalized PPI deficits when data across startle intensities were collapsed. Additionally, HIV-1Tgs exhibited lower PPI than F344s. c) Within-subjects, all rats had decreased startle responses to pulse-alone trials as the testing session progressed (HABIT1>P120>HABIT2). No other main effects or interactions were observed on ASR. Data presented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001; ns = not significant
