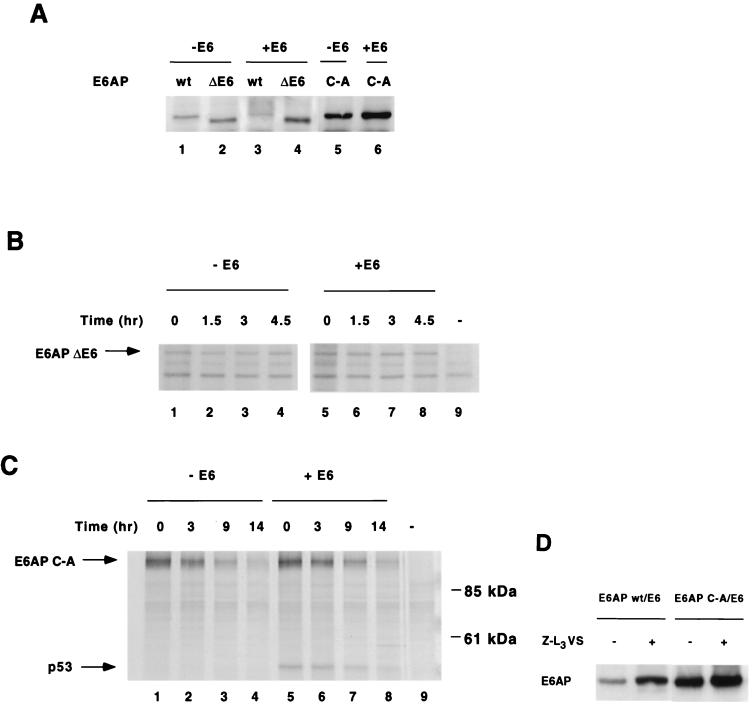
FIG. 6.
E6-mediated E6AP degradation in human cells requires E6-E6AP interaction, E6AP catalytic activity, and proteasome function. (A) Effect of E6 on steady-state levels of E6AP wild-type, ΔE6, and C-A. HA-E6AP isoform I (wild-type, ΔE6, or C-A mutant) was transfected with or without AU1-E6 into C33A cells. Cells were harvested 48 h posttransfection and immunoblotted for HA-E6AP with the 12CA5 antibody. (B and C) E6 expression does not affect the degradation rate of transfected E6AP ΔE6 (B) or C-A mutants (C) in C33A cells. Pulse-chase analysis of E6AP ΔE6 and C-A in the absence or presence of E6 was performed as in Fig. 2. Endogenous p53 immunoprecipitates with E6AP C-A in the presence of E6 as shown. (D) Steady-state levels of E6AP wild-type and C-A mutant in the presence of the proteasome inhibitor Z-L3VS. C33A cells were cotransfected with AU1-E6 and either HA-E6AP wild type or C-A. At 36 h posttransfection, transfected cells were treated for 14 h with either 50 μM Z-L3VS in DMSO or DMSO alone as a negative control. Cells were harvested, separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the 12CA5 antibody.