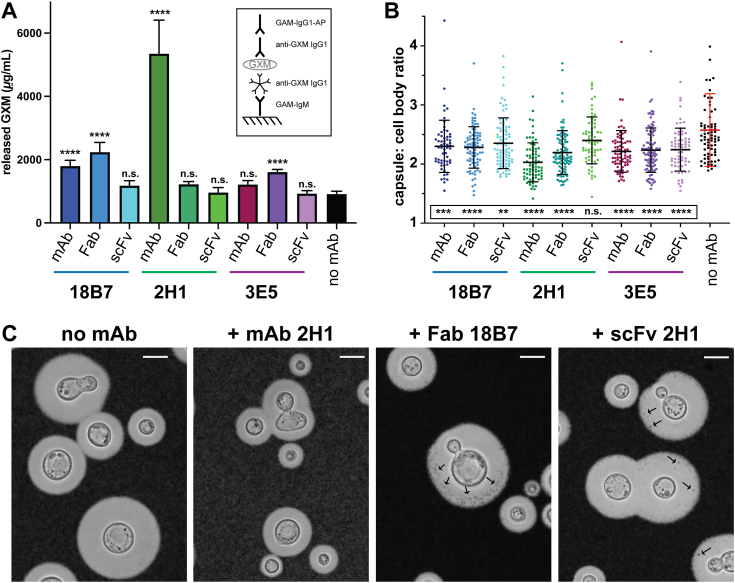
Figure 4.
Glycolytic activity of antibody fragments. Strain H99 cryptococcal cells were incubated with each antibody fragment for a period of 7 days and catalytic capsule cleavage was assessed. A, released capsular GXM concentrations measured by capture ELISA in reaction supernatants after antibody incubation. B, the diameters of cell bodies and capsules after antibody incubation were assessed. The ratio of capsule to cell body diameter are displayed for each condition. The mean ratios ± 1 SD are overlaid for each group. Each group contained at least 100 capsule measurements. Statistical significance of released polysaccharide and capsule diameter measurements with respect to ‘no mAb’ controls were determined by ordinary one-way ANOVA (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗p < 0.01; ns, not significant). C, representative microscopy images of cryptococcal cells in India Ink after incubation in PBS for 7 days alone or with mAb 2H1, Fab 18B7 and scFv 2H1. Arrows indicate the appearance of dark spots inside the capsules of C. neoformans cells incubated with Ab indicating India Ink penetrance into damaged regions of capsule. White scale bars on all microscopy images indicate 10 μm.