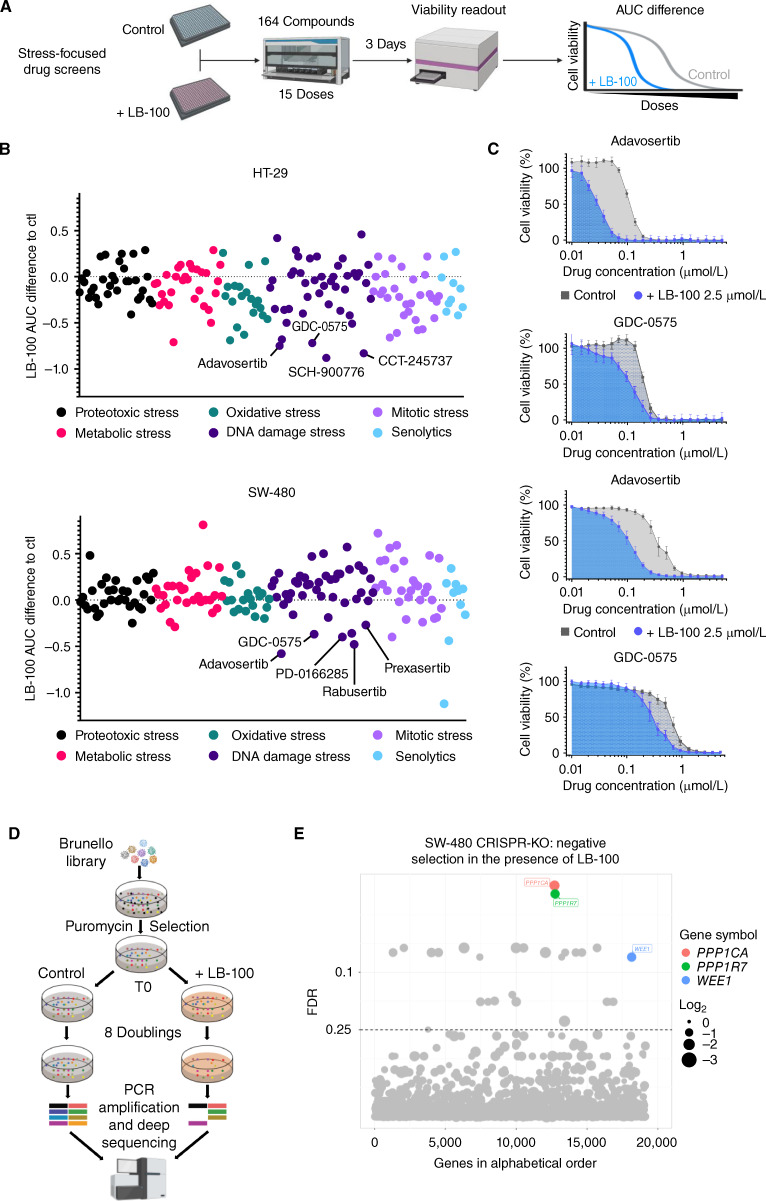
Figure 2.
Stress-focused drug screen and genome-wide CRISPR screen converge to identify synthetic lethality between LB-100 and WEE1 inhibition. A, Schematic outline of the stress-focused drug screen. B, AUC difference for each compound in the presence of LB-100 (2.5 μmol/L) relative to untreated controls in HT-29 and SW-480 cells. In both cases, WEE1 and CHK1 inhibitors are annotated. C, Dose–response curves comparing the normalized AUC for adavosertib or GDC-0575 in the presence or absence of LB-100 (2.5 μmol/L) in HT-29 and SW-480 cells. Cell viability was estimated by resazurin fluorescence after 3 days in the presence of the drugs. D, Schematic outline of the CRISPR-KO screen. E, The bubble plot shows gRNAs significantly depleted in the LB-100–treated (2.5 μmol/L) arm compared with the untreated controls. Four different gRNAs per gene were tested in 3 replicates. Cells on both conditions were grown for at least 8 population doublings before DNA harvesting and sequencing. Hits were called based on a 0.25 false discovery rate (FDR) and at least 1 log2 fold-change difference between treated and untreated samples. Only the hits mentioned in the main text are named and colored, the full list of hits is presented in Supplementary Table S7.