Figure 4.
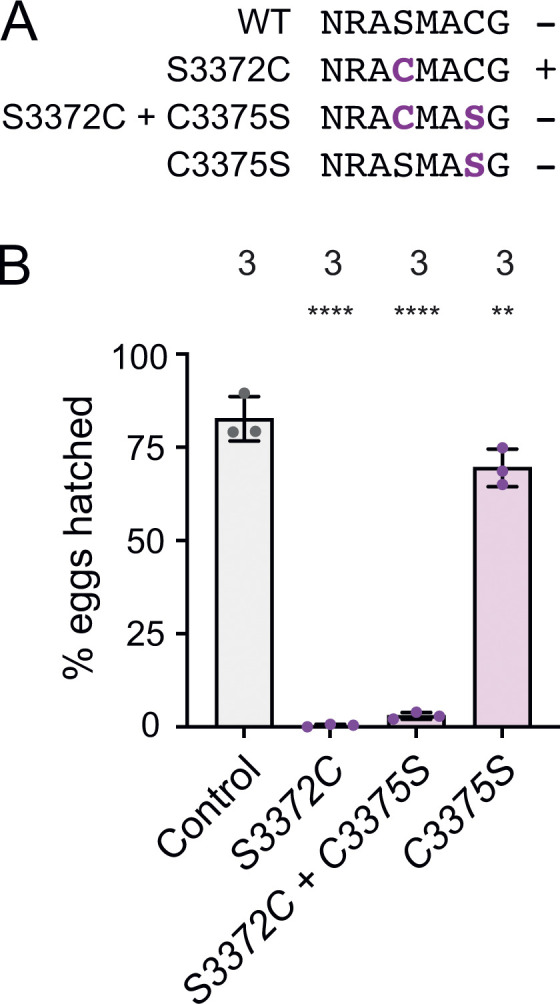
The S3372C embryonic arrest is not caused by ectopic disulfide bonding in Dhc. (A) Sequences of relevant regions of wild-type (WT), S3372C, S3372C + C3375S, and C3375S Drosophila Dhc. Mutated residues are shown in bold magenta. The potential for intramolecular disulfide bond formation is indicated with +. (B) Quantification of hatching frequency of eggs laid by mated females of the indicated genotypes. Columns show mean values per egg collection; error bars represent SD; circles are values for individual egg collections. Numbers of collections per genotype (each from an independent cross; 245–736 eggs per collection) shown above bars. The control genotype was homozygous for a wild-type Dhc allele recovered from the same CRISPR-Cas9 mutagenesis experiment that generated the Dhc mutant alleles. Evaluation of statistical significance (compared to control) was performed with a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: ****, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.01.
