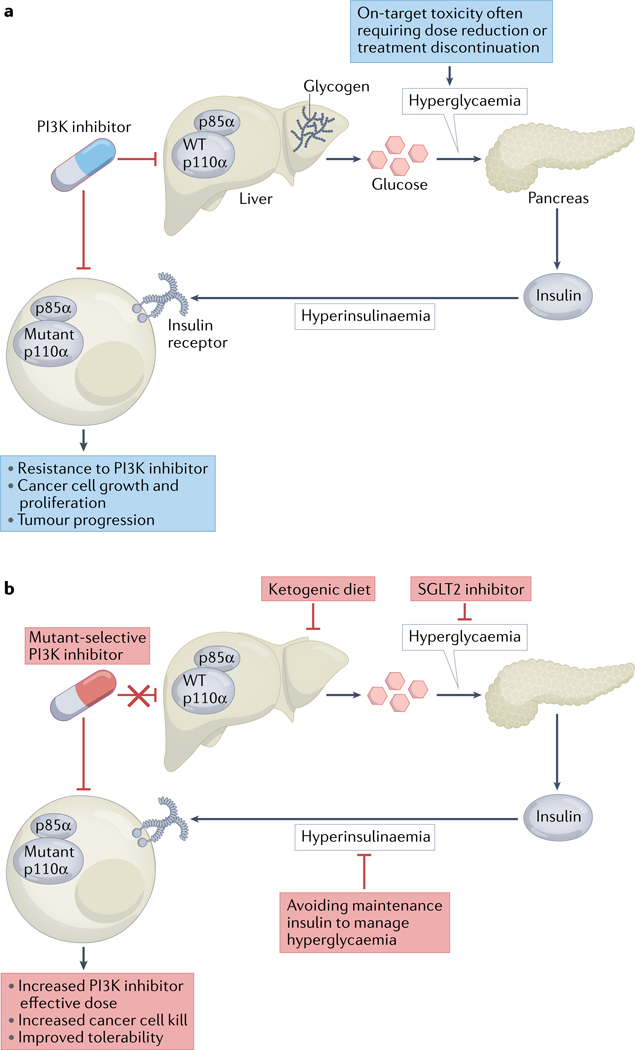
Fig. 4 |. Metabolic mechanisms limiting the efficacy of PI3K inhibitors.
a | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors suppress the activity of not only mutant PI3K in cancer cells but also wild-type (WT) PI3K in non-malignant cells of the liver and other tissues, leading to decreased glucose uptake, hyperglycaemia, and compensatory insulin secretion by the pancreas and thus hyperinsulinaemia. As a result, insulin receptor signalling can restimulate the growth and proliferation of cancer cells, thus attenuating the effects of PI3K inhibitors. b | A ketogenic diet, sodium–glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, mutant-selective PI3K inhibitors and avoidance of maintenance insulin to manage hyperglycaemia are predicted to increase the effective dose, anticancer effects and tolerability of PI3K inhibitors.