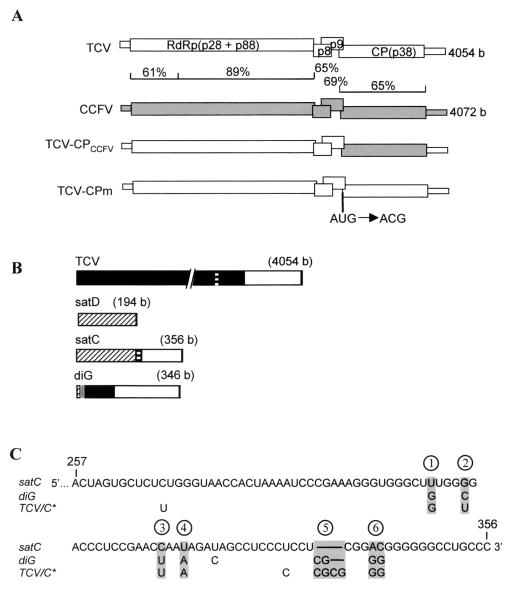
FIG. 1.
Genomic and subviral RNAs used in this study. (A) Genomic RNAs. ORFs and untranslated regions are represented by thick and thin boxes, respectively. The percent sequence similarity between TCV and CCFV genomes is shown. TCV-CPm has a point mutation in the CP initiation codon as indicated, which causes translation initiation at an upstream CUG codon resulting in two additional N-terminal amino acids and a reduction in CP levels to 20% of that of the wt (54). (B) Subviral RNAs associated with TCV. Similar sequences among TCV genomic and subviral RNAs are shaded alike. The sizes of the RNAs are given. (C) Alignment of the 3′-end sequences of satC, diG, and the TCV genomic RNA, which is identical to satC* (TCV/C∗) (16). Only differences among the RNAs are indicated. Lines indicate absence of the bases in satC and diG, compared with TCV or satC∗. The six positional differences between satC and diG are shaded. The last two positions (5 and 6) each have two consecutive nucleotide differences between the two subviral RNAs.