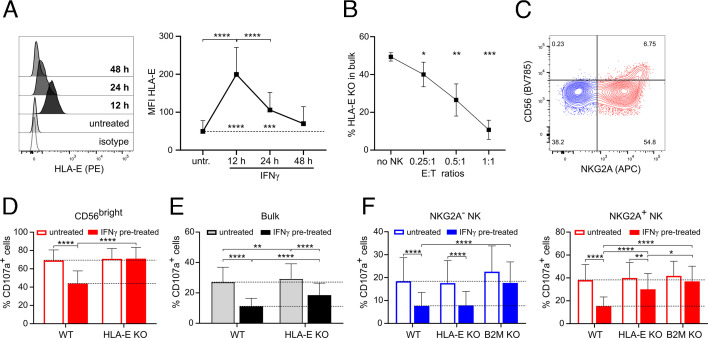
Figure 2.
IFNγ-induced expression of HLA-E on A375 cells inhibits NKG2A+ NK cells. (A) Expression of HLA-E on A375 cells treated or not with IFNγ for 12, 24 and 48 hours (n=6). (B) Reduction in HLA-E KO cell population after 24 hours of co-culture of NK cells with mixed WT:HLA-E KO cells (1:1) at different E:T ratios (n=6). (C) Representative dot plot showing the expression of NKG2A and CD56 on NK cells. (D, E) Degranulation of CD56bright (D) and bulk NK cells (E) after 4 hours of co-culture with HLA-E KO or WT A375 cells. A375 cells were pretreated or not o/n with IFNγ (n=11). (F) Degranulation of NKG2A− and NKG2A+ NK cells after 4 hours of co-culture with WT, HLA-E KO and B2M KO A375 cells pretreated or not with IFNγ 12 hours before the co-culture (n=6–9). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA (multiple comparisons) test (A, B, D, E, F), *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. ANOVA, analysis of variance; E:T, effector to target; KO, knockout; NK, natural killer; WT, wild-type.