FIGURE 2.
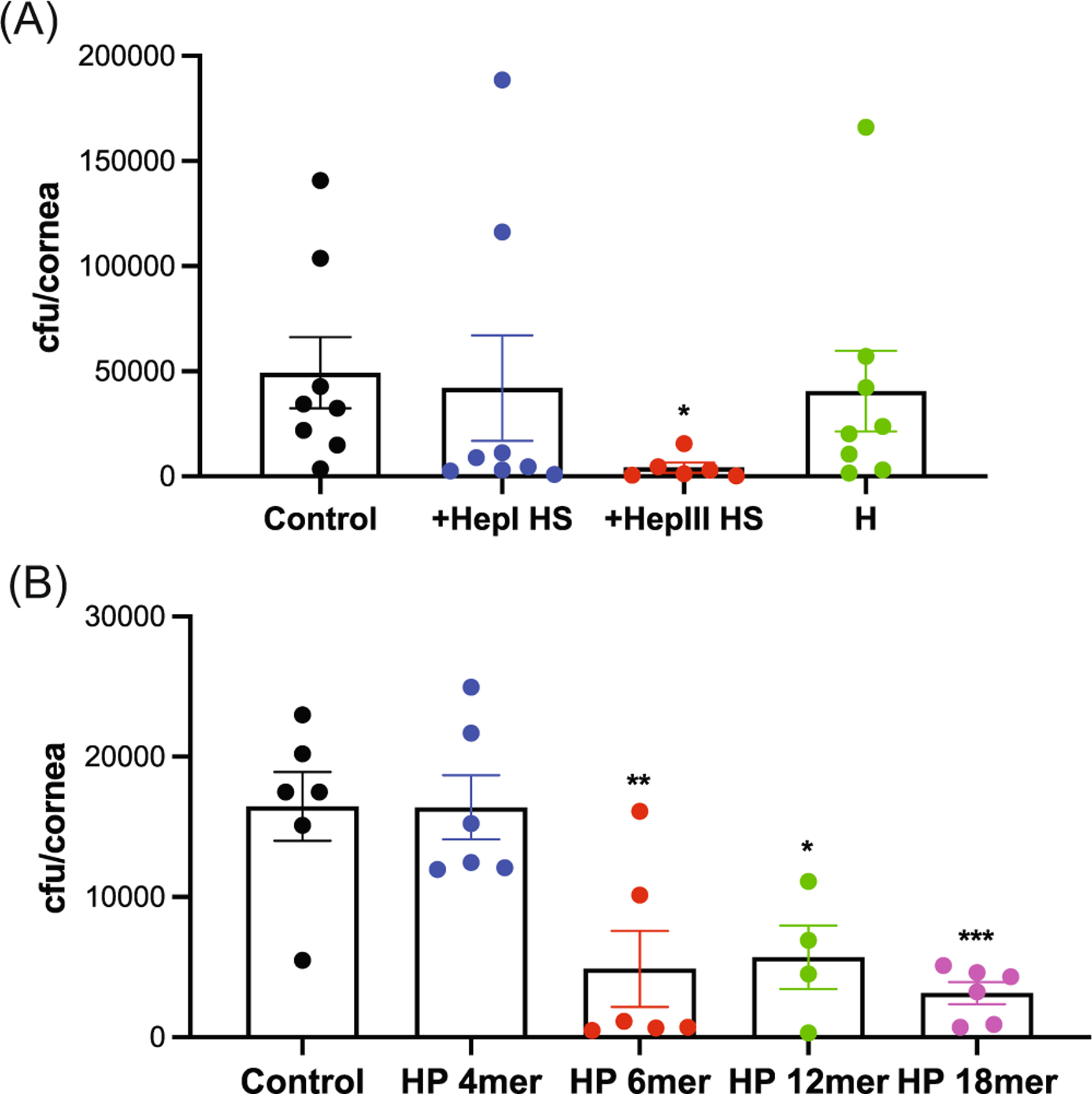
Sulfated heparan compounds inhibit Streptococcus pneumoniae corneal infection. (A) Injured corneas were topically coinfected with 108 cfu of S. pneumoniae TIGR4 and PBS (control) or 200 ng of heparinase I-digested HS (HepI HS), heparinase III-digested HS (HepIII HS), or heparosan (H) and the corneal bacterial burden was measured at 6 h pi (mean ± SE, n = 6–8, *p < 0.05). (B) Injured corneas were topically coinfected with 108 cfu of TIGR4 and HP 4-mer (800 ng), 6-mer (500 ng), 12-mer (400 ng), or 18-mer (200 ng) oligosaccharides and the corneal bacterial burden was assessed at 6 h pi (mean ± SE, n = 4–6, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). HP, heparin; HS, heparan sulfate; pi, postinfection.
