FIGURE 3.
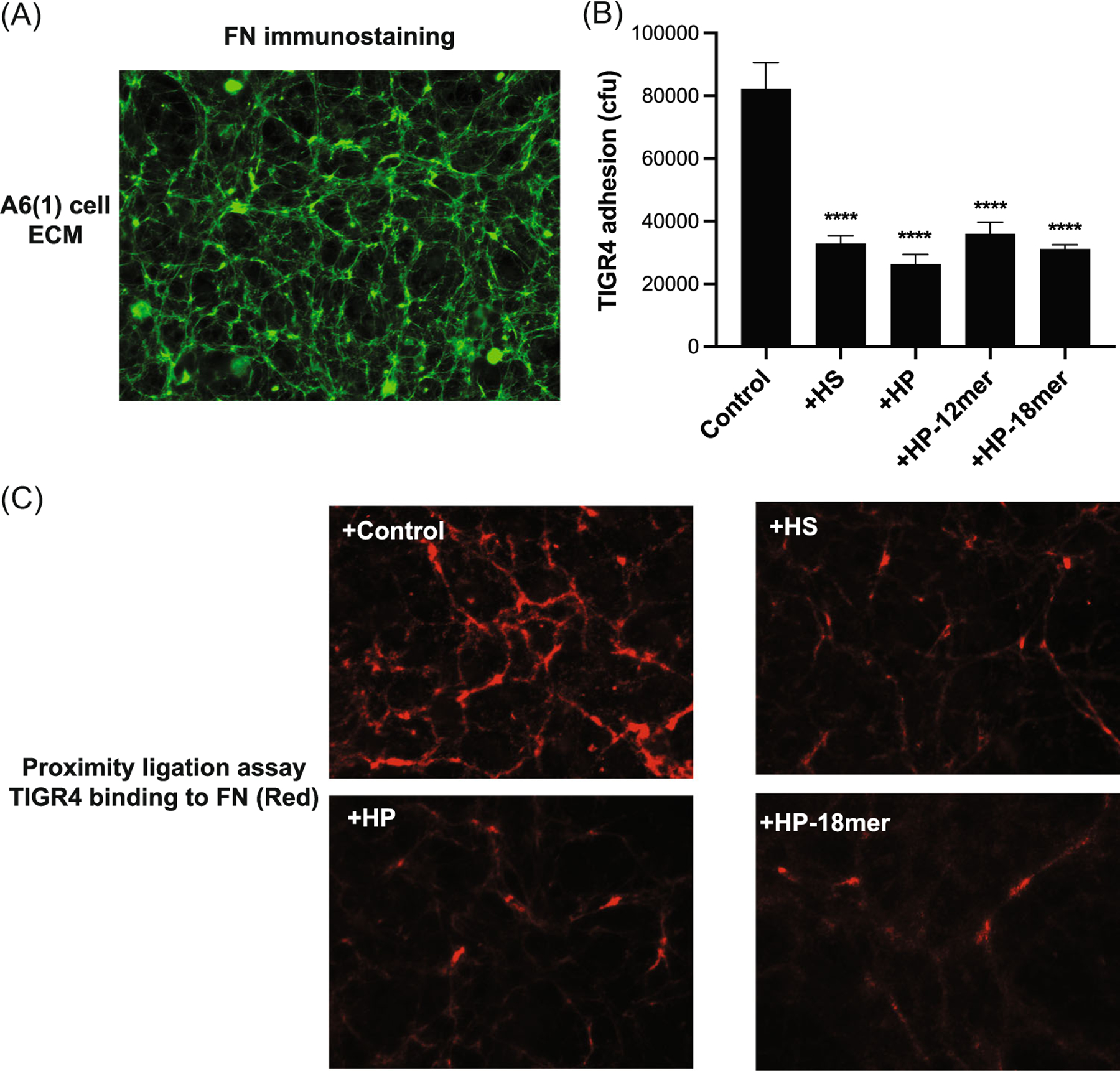
HS, HP, and HP oligosaccharides inhibit Streptococcus pneumoniae adhesion onto FN fibrils in the ECM of cultured corneal epithelial cells. A6(1) corneal epithelial cells were seeded at 30% confluence and cultured for 6 days and decellularized. (A) The decellularized ECM was fixed with 4% formaldehyde, blocked, and immunostained with anti-FN and Alexa 488 secondary antibodies. Images were captured with a Zeiss Axiovert 40 CFL microscope and AxioCam high-resolution camera (original magnification, ×200). (B) The decellularized ECM of confluent A6(1) corneal epithelial cells was incubated with PBS (control) or 5 μg/mL of HS, HP, HP 12-mer, or HP 18-mer for 30 min and 5× 105 cfu of S. pneumoniae TIGR4 was added and incubated for another 1 h. (B) Attached bacteria were quantified by plating out serial dilutions of detergent extracts and counting the number of colonies (mean ± SE, n = 5, ****p < 0.0001, ANOVA). (C) Binding of S. pneumoniae to FN fibrils in the decellularized ECM of A6(1) cells treated without or with 5 μg/mL HS, HP, or HP 18-mer was assessed by PLA using anti-FN and anti-PNAG antibodies. Red indicates where the distance between TIGR4 and FN is ≤40 nm (original magnification, ×400). ANOVA, analysis of variance; ECM, extracellular matrix; FN, fibronectin; HP, heparin; HS, heparan sulfate; PNAG, poly-N-acetylglucosamine.
