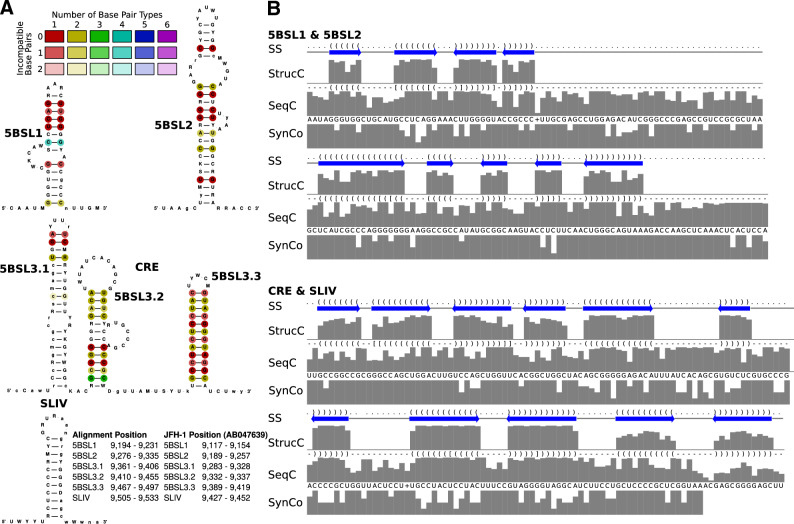
Figure 1.
Known RNA secondary structures in the downstream NS5B coding region including the cis-replication element (CRE, 5BSL3.2) which are relevant for replication control. (A) RNA secondary structures are colored by the number of base pair types illustrating the extent of covariations in double-stranded regions. The SL IV (or 5BSL3.4) contains the NS5B stop codon in the apical loop. The structure was visualized using R2DT59. The nucleotide sequence shows the most informative sequence (IUPAC code) calculated by RNAalifold60 based on the alignment. Lowercase letters indicate gaps in the alignment column. (B) RNA secondary structure dot-bracket annotation (SS), structure consensus (StrucC), sequence consensus (SeqC), and the fraction of nucleotides used from synonymous codons (SynCo). Thereby, a low value indicates that only a few nucleotide(s) out of all nucleotides possible for synonymous codons are actually used by the different HCV isolates, indicating a high degree of primary sequence conservation which goes beyond the requirements of the coding sequence. This provides evidence that a conserved functional RNA element may overlap with the coding sequence. Alignments shown in Figs. S12 and S13.