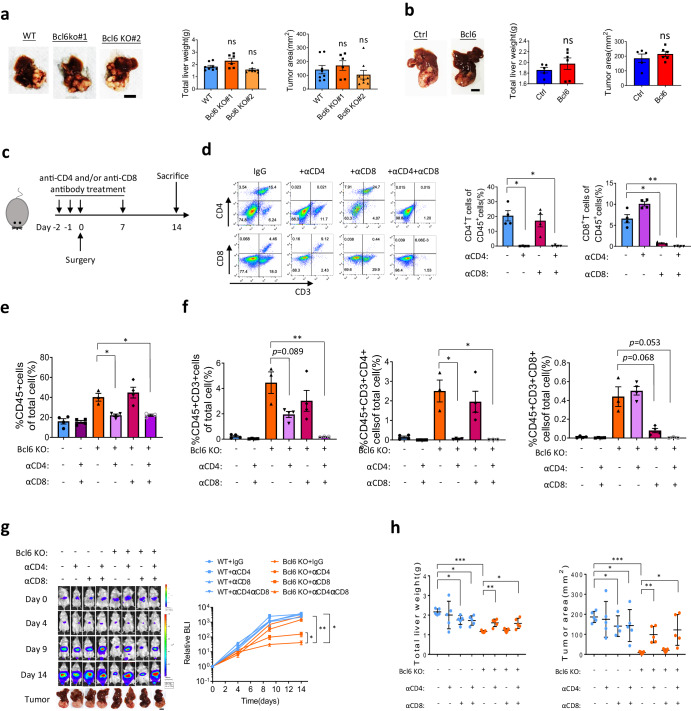
Fig. 5. BCL6 suppresses CD4+ T cells mediated tumor immune surveillance.
a Liver tumor image, liver weight and tumor volume after transplantation of H22 in nude mice for 2 weeks, n = 7–8. b Liver tumor image, quantification of liver weight and tumor volume after transplantation of Hepa1-6 in nude mice for 1 month, n = 5–6. c Schematic of experiment design. d Flow cytometry for blood T cell depletion efficiency and specificity at 2 weeks after treatment with anti-CD4 (aCD4) and/or anti-CD8 (aCD8) antibodies, n = 4 per group. Flow cytometry quantification of H22-derived tumor immune cell infiltration (e) and T cell infiltration (f) after antibody treatment, n = 3–4 per group. g In vivo imaging as well as liver cancer images for H22 derived tumor growth after antibodies treatment, n = 5 per group. h Quantification of total liver weight and tumor area after treatment of depletion antibodies at 2 weeks post-surgery, n = 5 per group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns: not significant, tumor image scale: 10 mm.