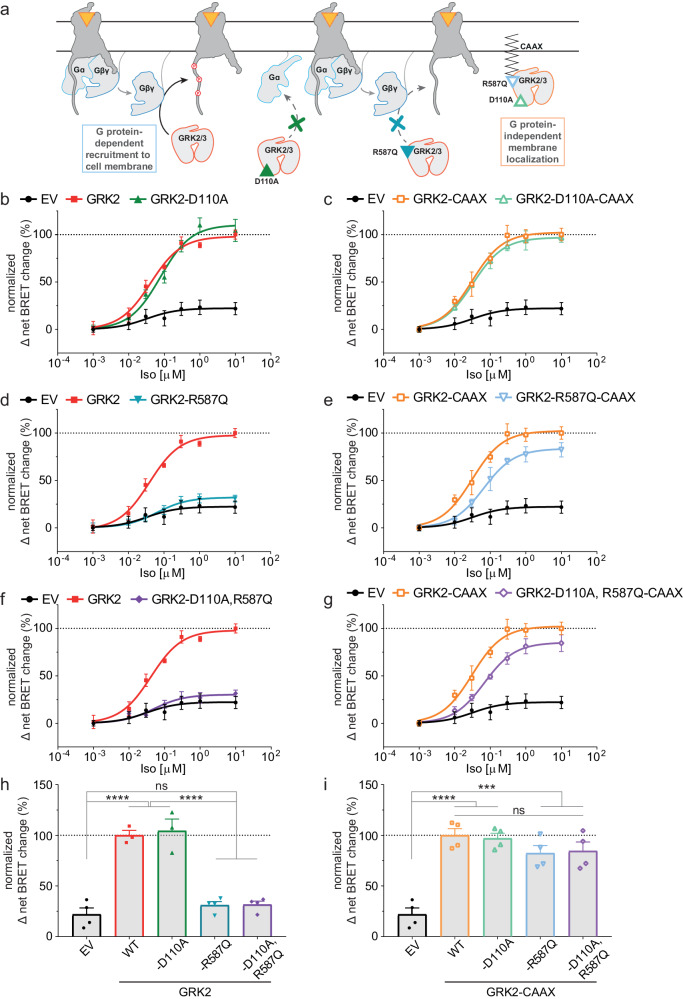
Fig. 1. GRK2-mediated β-arrestin2 recruitment to the beta-2 adrenergic receptor (b2AR) is dependent on the membrane localization of the GRK.
a Schematic representation of the utilized GRK mutants D110A (interrupting the GRK2/3–Gα interaction), R587Q (interrupting the GRK2/3–Gβγ interaction) and the double mutant (D110A, R587Q), also as versions with a CAAX box to localize GRK2/3 to the plasma membrane independent of the G protein interaction. b–g Isoproterenol (Iso)-induced Halo-Tag-β-arrestin2 recruitment to b2AR-NanoLuciferase (NLuc) in GRK2/3/5/6-depleted quadruple knockout HEK293 (ΔQ-GRK) cells in absence of the ubiquitously expressed GRKs (empty vector (EV)-transfected) and in presence of wild type (WT) GRK2 or either GRK2-D110A (b), GRK2-R587Q (d) or GRK2-D110A,R587Q (f). The same experiment was performed with the corresponding GRK2-CAAX versions (c, e, g). All data are shown as Δ net BRET change in percent of n = 4 (except WT GRK2 (a) and GRK2-D110A (b) which are n = 3) independent experiments ± SEM, normalized to the maximum response with GRK2 (b, d, f) or GRK2-CAAX (c, e, g). The curves in absence of ubiquitously expressed GRKs (EV), GRK2 and GRK2-CAAX are shown multiple times to allow direct comparisons. h, i Normalized BRET data of the highest stimulation of b-g are displayed as bar graphs and statistical differences were tested using one-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey’s test (ns not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001). Detailed statistical results are provided in Supplementary Table 2.