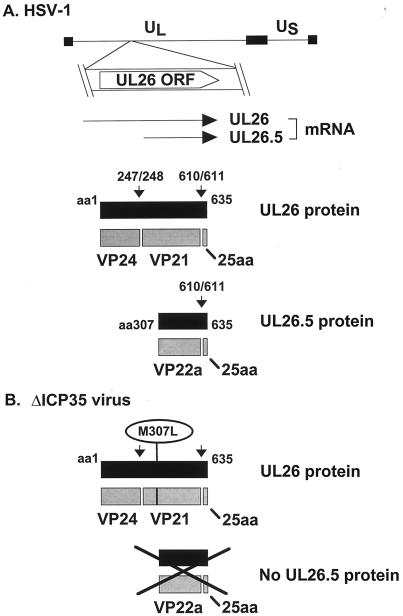
FIG. 1.
HSV-1 UL26 and UL26.5 gene products. (A) The UL26 open reading frame is indicated below its location in the prototype orientation of the HSV-1 genome (shown with thin line representing unique long [UL] and unique short [US] regions bounded by terminal repeated sequences, represented by thick bars). UL26 and UL26.5 mRNA transcripts and protein products are also depicted. Primary translation products are represented by solid boxes. Gray boxes represent proteolysis products. Vertical arrows indicate the sites of proteolytic processing of the scaffold proteins (14). Numbers indicate aa residues at the N and C termini of the polypeptides or the sites of proteolytic processing. (B) Structure of the ΔICP35 mutant virus and its predicted protein products. Mutation of Met-307 of UL26 to Leu prevents translation of the UL26.5 protein (31). A black X covers the products whose translation is prevented by the M307L mutation.