Figure 6.
T1-DANs function through dopaminergic activation of PB-LNs
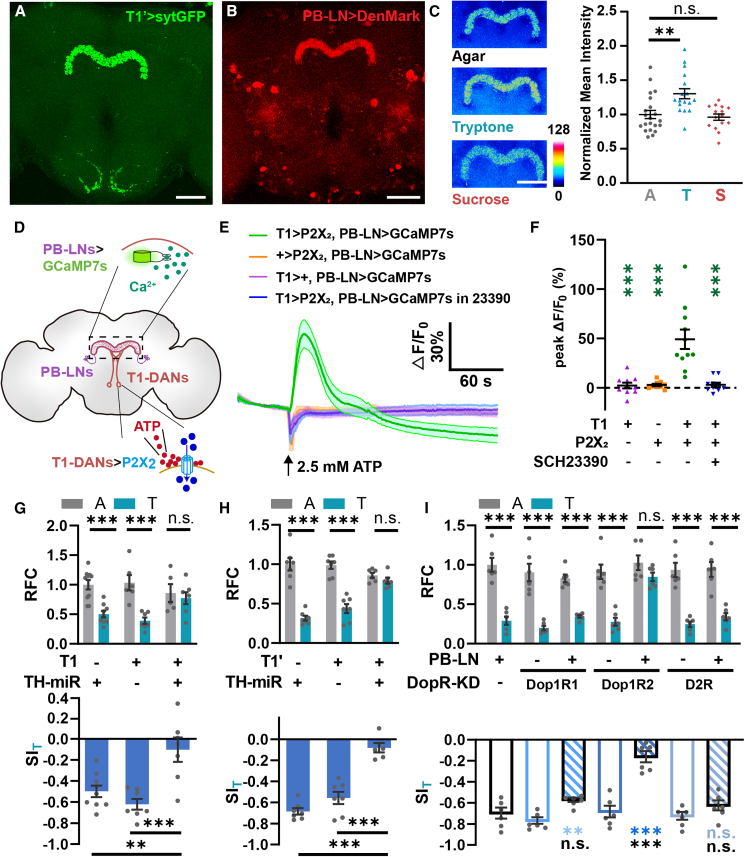
(A and B) The pre-synaptic signals of T1-DANs (A) and the postsynaptic sites of PB-LNs (B) are both concentrated in the brain region of PB. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(C) The syb:GRASP signals between T1-DANs and PB-LNs increased after protein consumption. Scale bar, 50 μm. The number of brains: n = 15–21.
(D–F) T1 activation induced a significant increase in calcium signals in PB-LNs. This induction was abolished when the antagonist of the dopamine D1-like receptor SCH23390 was supplied. The projection region of PB-LNs was selected as the ROI. The number of brains: n = 9–11.
(G and H) Knocking down TH in T1-DANs abolished PIFI effect. The number of trials: n = 5–10.
(I) KD of Dop1R2, but not Dop1R1 or D2R, in PB-LNs abolished PIFI effect. The number of trials: n = 6.
One-way ANOVA, Dunnett test in (C) and (F). Student’s t test for RFC in (G)–(I). One-way ANOVA, Dunnett test for SI. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. n.s. indicates no statistical significance. The data are shown in mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S6.