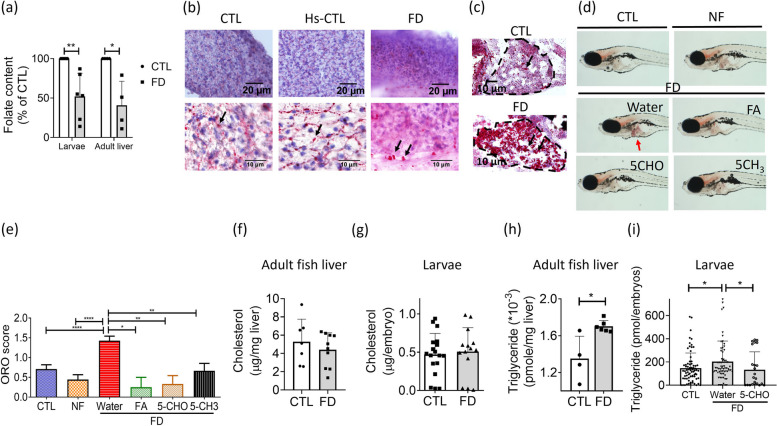
Fig. 2.
Increased lipid accumulation was found in FD zebrafish liver. The transgenic larvae and adult fish were induced for FD and examined for their hepatic lipid deposition. a The liver of larvae of 11 dpf and adult fish after completing FD-induction protocols were collected and subjected to microbiology assay. Data were collected from 6 and 4 independent experiments for larval liver and adult fish liver, respectively. b-c The cryosections prepared from adult fish liver (b) and whole larvae (c) were examined for lipid deposition (black arrows) with Oil Red O staining. d-e The hepatic lipid accumulation (red arrow) in larvae at 11 dpf, with/without FA, 5-CHO-THF, and 5-CH3-THF supplementation, were stained with Oil Red O (red arrow) (d) and scored (e) following the criteria based on the percentage of intensely stained area occupied in larval liver: less than 30% (1), between 30% to 70% (2), or more than 70% (3). Those showed no significant staining signal was scored (0). Data were collected from at least 3 independent experiments. f-i Hepatic cholesterol (f-g) and triglyceride (h-i) in adult fish liver (f and h) and larvae at 11 dpf (g and i) were measured with colorimetric/fluorometric Assay. Significant increase was found for the triglyceride levels in both adult fish liver and larval liver. Supplementing with 5-CHO-THF effectively prevented the increase of triglyceride in FD larvae. All the data presented are the averages of at least three independent trials with 10-40 larvae or 4-10 adult fish livers for each group. CTL, control (Tg-GGH/LR larvae without FD); FD, folate deficiency; FA, folic acid; 5-CHO, 5-formyl-THF; 5-CH3, 5-methyl-THF. Statistical data are shown in mean ± SEM. * p<0.05, **, p <0.01; ****, p<0.0001