Figure 4. AXL-WRNIP1 interaction mediates replication stress response in Lat and M-BM cells.
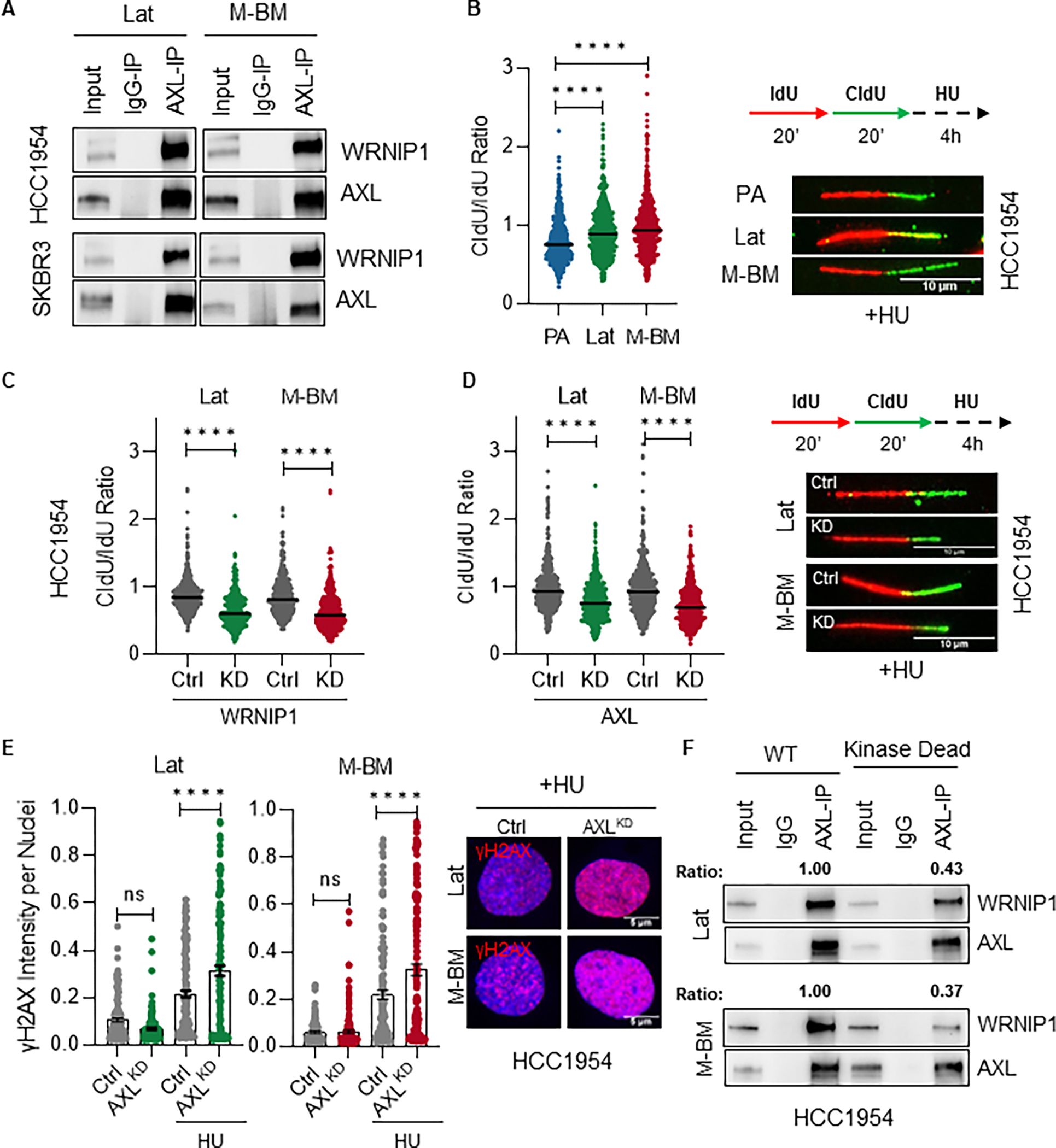
A, Immunoblot showing AXL-WRNIP1 interaction in HCC1954 Lat and M-BM cells under normal (Ctrl) and replication stress induced condition (in presence of 4mM HU for 5hrs). B, Relative fork degradation measured by the CldU/IdU ratio in presence of 4mM HU. Representative images of DNA fibers from HCC1954 PA, Lat and M-BM cells are also shown. IdU (red color) and CldU (green color). N = 3 for all experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Mann–Whitney U test, ****, P < 0.0001. C-D, Relative fork degradation measured by the CldU/IdU ratio in presence of 4mM HU upon WRNIP1 knockdown (WRNIP1KD) and AXL knockdown (AXLKD) in HCC1954 Lat and M-BM cells. Representative images of DNA fibers are also shown. IdU (red color) and CldU (green color). N = 3 for all experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Mann–Whitney U test, ****, P < 0.0001. E, γH2AX intensity quantification of HCC1954 Lat and M-BM cells treated with 4mM HU for 5hrs. Representative image of γH2AX intensity under HU. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was used, followed by the Dunnett test. ****, P < 0.001, ns: not significant. F, Immunoblot showing reduced interaction between kinase dead AXL and WRNIP1. This assay was performed by reintroducing AXL (WT) and kinase dead mutant in HCC1954 AXLKD Lat and M-BM cells. AXL immunoprecipitation was performed and ratio was determined by normalizing WRNIP1 expression to immune-precipitated AXL.
