Figure 1: Structure-inspired deorphanization of GPR161.
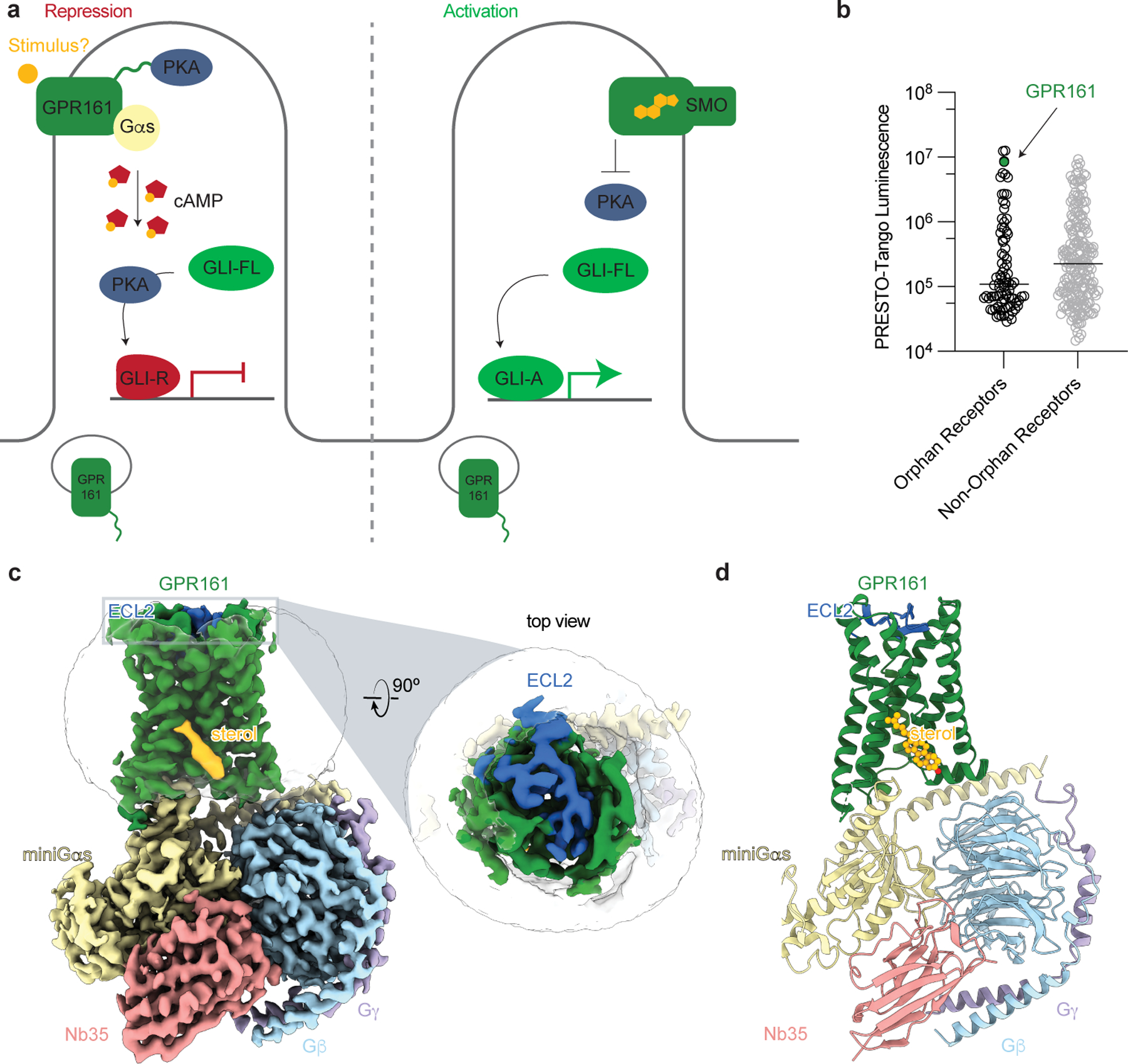
a) The Hedgehog pathway is regulated by two key GPCRs, GPR161 and Smoothened (SMO). In the absence of Hedgehog, GPR161 represses the pathway through constitutive cAMP signaling from an unknown stimulus. In the presence of Hedgehog, SMO activates the pathway by entering the cilia, binding cholesterol, and inhibiting PKA, while GPR161 exits cilia. b) GPR161 yields an exceptionally strong signal for β-arrestin recruitment in the PRESTO-Tango assay when compared across 314 GPCRs (data replotted from Kroeze WM et al 201522, n = 4 for each target, shown as mean ± s.e.m. of technical replicates). This assay is performed in a modified HEK293 cell line, suggesting that GPR161 is constitutively active under heterologous expression conditions. c) Cryo-EM density map of GPR161 in complex with Gs heterotrimer (miniGαs, Gβ, and Gγ) and stabilizing nanobody 35 (Nb35). The map reveals a density consistent with the shape of a sterol (yellow) and an extracellular loop 2 (ECL2, blue) that is packed within the seven transmembrane core of GPR161. d) Ribbon diagram of activated GPR161 heterotrimer complex. Cholesterol is modeled into the sterol density (yellow).
