Figure 5: GPR161 PKA-RI binding, but not cAMP generation, is necessary to repress ciliary trafficking of GLI2.
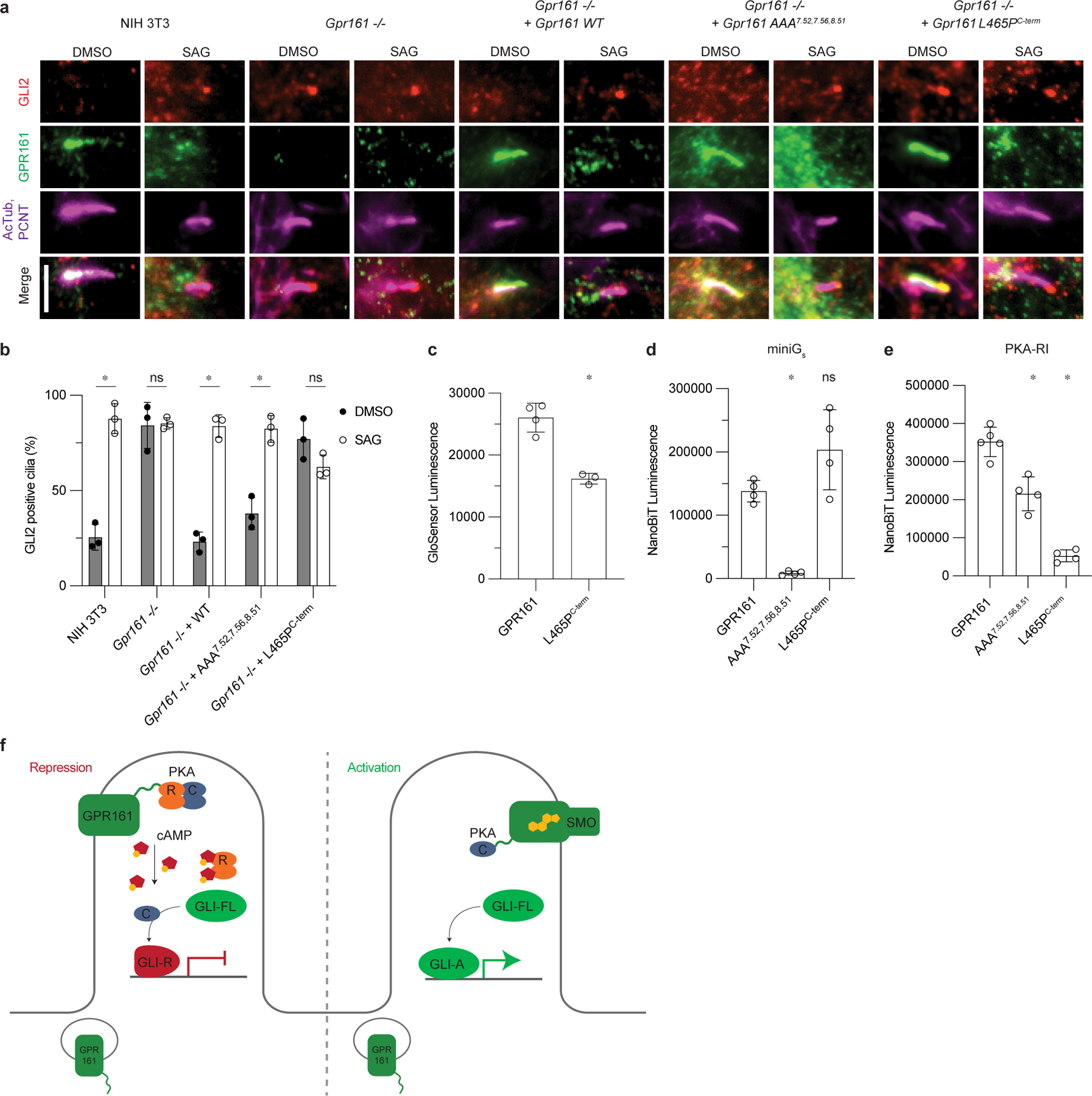
a) Representative images of GPR161 and mutants on ciliary localization and GLI2 repression in ciliary tips in NIH 3T3 cells. NIH 3T3 Flp-In CRISPR based Gpr161−/− cells stably expressing untagged mouse wild-type or Gpr161 mutants were starved for 24 hr upon confluence and were treated for further 24 hr ± SAG. Cells were immunostained with anti-GLI2 (red), anti-GPR161 (green), anti-acetylated, and centrosome (AcTub; PCNT purple) antibodies. Scale bar, 5 µm. b) Quantification GLI2 positive cilia indicating Hedgehog pathway activation. AAA7.52, 7.56, 8.51 rescues function similar to WT, and L465PC-term does not, similar to Gpr161−/−. Data are shown from n=3 biologically independent experiments from images taken from 2–3 different regions/experiment and counting 15–30 cells/region. Data are mean±s.d. (*P < 0.05; ns, not significant; two-way ANOVA followed by Šidák’s multiple comparison tests; adjusted P values for DMSO vs. SAG: NIH3T3=<0.0001, Gpr161−/−=>0.9999, Gpr161−/− + WT or AAA7.52, 7.56, 8.51=<0.0001, Gpr161−/− + L465PC-term=0.1459). c) cAMP production assay assessing L465PC-term mutation. Data are mean±sd, n=3 (for L465PC-term) or n=4 (for GPR161) biologically independent samples (*P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests; adjusted P value for GPR161 vs. L465PC-term=<0.0001). d) Nanoluc complementation assay for receptor recruitment of miniGs. Both GPR161 and L465PC-term constitutively recruit miniGs while AAA7.52,7.56,8.51 does not. Data are mean±sd, n=4 biologically independent samples (*P < 0.05; ns, not significant; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests; adjusted P values: GPR161 vs. AAA7.52,7.56,8.51=0.0018, GPR161 vs. L465PC-term=0.0656). e) Nanoluc complementation assay for receptor recruitment of PKA-RI. GPR161, AAA7.52, 7.56, 8.51, and L465PC-term each recruit less PKA-RI, respectively. Data are mean±sd, n=4 (for AAA7.52,7.56,8.51 and L465PC-term) or n=5 (for GPR161) biologically independent samples (*P < 0.05; ns, not significant; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison tests; adjusted P values; GPR161 vs. AAA7.52,7.56,8.51= 0.0004, GPR161 vs. L465PC-term=<0.0001). f) PKA-centric model of Hedgehog pathway repression in cilia. In the absence of Hedgehog, GPR161 represses the pathway in cilia through coupling PKA. GPR161 also functions in periciliary endosomal compartments in regulating GLI-R formation3. In the presence of Hedgehog, SMO activates the pathway by entering the cilia, binding cholesterol, and sequestering PKA-C, while GPR161 exits cilia.
