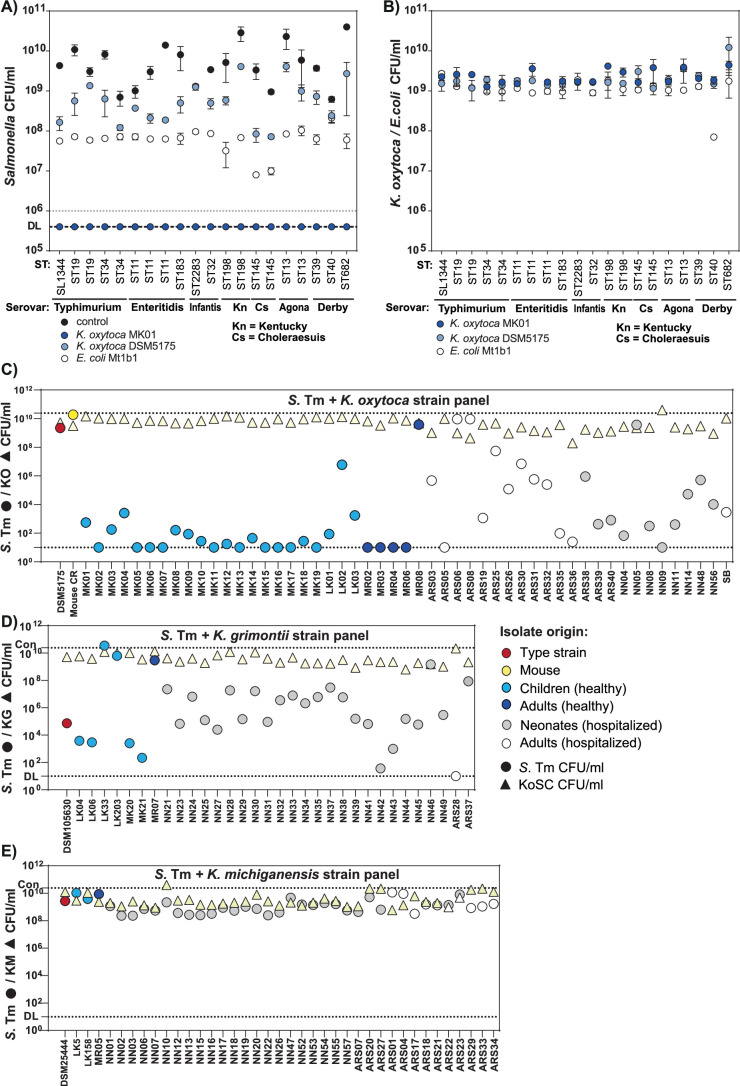
Extended Data Fig. 3. Broad protective capability is shared among many K. oxytoca and K. grimontii but not K. michiganensis strains from different origins.
(a) S. enterica and (b) Enterobacteria (K. oxytoca MK01/DSM5175T, E. coli Mt1b1) CFUs after 24 h of co-cultivation. Dashed line indicates level of detection (DL). (a-b) The mean ± SEM of two independent biological experiments with n = 2 technical replicates are displayed. (c) Resulting S. Tm (dots) and KoSC (triangles) CFUs of co-cultures with various strains from the KoSC, including K. oxytoca = KO, (d) K. grimontii = KG and (e) K. michiganensis = KM. The different colors of each dot represent the origin of the KoSC isolate in each co-culture (type strains = red star, mouse gut isolate = yellow dot, healthy children = light blue dot, healthy adults = dark blue dot, neonatal isolate from medical environment = light grey dot and adult isolate from medical environment = white dot). Dots represent the levels of S. Tm in each co-culture, while triangles represent the corresponding CFUs of the KoSC strain in each condition. (c-e) The mean of 2 (K. grimontii) or 3 (K. oxytoca / K. michiganensis panel) independent biological experiments with n = 2 technical replicates are displayed.