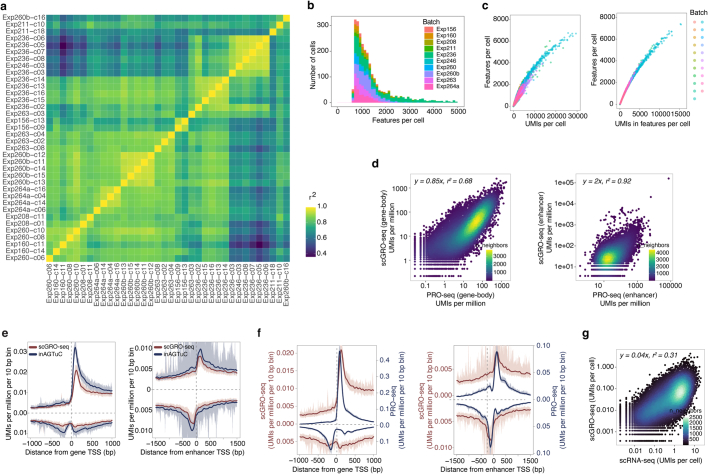
Extended Data Fig. 7. Additional benchmarking of scGRO-seq.
a, Coefficient of determination (r2) between each 96-well plate from scGRO-seq batches that passed the quality-control threshold. r2 was calculated from average UMIs per 96 cells in all genes and enhancers. b, Distribution of scGRO-seq features (genes + enhancers) per cell. c, Relationship between the number of features detected per cell and the UMIs per cell (left) or UMIs in features per cell (right) in scGRO-seq. Colors indicate different batches of scGRO-seq. d, Correlation between scGRO-seq and PRO-seq UMIs per million sequences in gene bodies (left, n = 19,961) and enhancers (right, n = 12,542). UMIs from the 500 bp regions from each end of the genes and 250 bp regions from each end of the enhancers were removed to only include nascent RNA from elongating RNA polymerases, and the data was plotted on a log-log scale to show the range of data distribution. e, Metagene profiles of scGRO-seq compared with inAGTuC UMIs per million per 10 base pair bins around the TSS of genes (left, n = 19,961) and enhancers (right, n = 12,542). The line represents the mean, and the shaded region represents the 95% confidence interval. f, Comparison of metagene profiles between scGRO-seq and PRO-seq UMIs per million per 10 base pair bins around the TSS of genes (left, n = 19,961) and enhancers (right, n = 12,542). The line represents the mean, and the shaded region represents 95% confidence interval. g, Correlation between scGRO-seq and scRNA-seq UMIs per cell in the body of genes (left, n = 19,961). UMIs from the 500 bp regions from each end of the genes were removed to only include nascent RNA from elongating RNA polymerases, and the data was plotted on a log-log scale to show the range of data distribution.