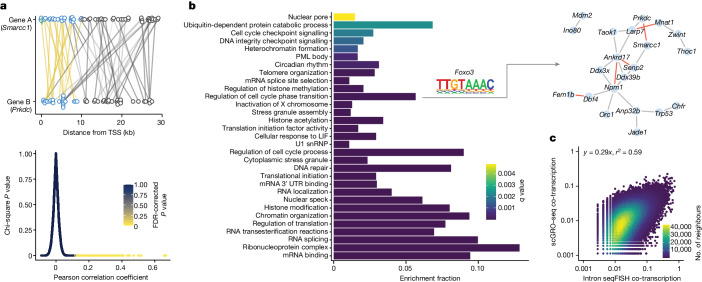
Fig. 4. Coordinated transcription of functionally related genes.
a, Top, a pair of co-transcribed genes. Reads within the first 10 kb of the gene pair (blue circle) expressed in the same cells are connected by a yellow line. Reads beyond the first 10 kb (grey circles and lines) were not used in the gene–gene correlation. Bottom, pair-wise Pearson correlation was calculated from a binarized genes by cells matrix. The relationship among the Pearson correlation coefficient, uncorrected chi-square P value and the FDR-corrected P value using the Benjamini–Hochberg correction method for pairwise gene–gene correlation. b, Gene ontology (GO) terms enriched in co-transcribed gene modules. The transcription factor motif enriched in the promoters of genes associated with the GO term and the co-transcribed genes that contributed to the enrichment of the GO term is shown as an example on the right (red line indicating ρ > 0.15). A complete list of GO terms and the co-transcribed genes contributing to the enrichment of the GO terms is provided in Supplementary Table 5. c, Correlation of co-transcription of significantly co-transcribed gene pairs (n = 164,380) between scGRO–seq and intron seqFISH data. Axes represent the fraction of cells in which a gene pair is co-transcribed.