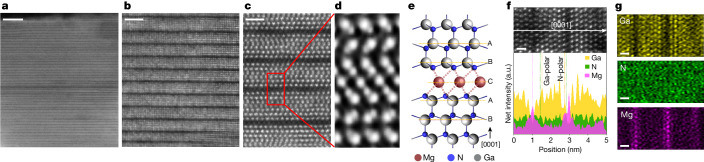
Fig. 1. Mg-intercalated GaN superlattices.
a–c, Cross-sectional HAADF-STEM images with progressively magnified views reveal the typical structure of 2D-Mg-intercalated GaN superlattices. The dark lines indicate monoatomic 2D-Mgi sheets and are perpendicular to the c axis (the [0001] direction). d, An iDPC-STEM image (magnified view of the region in the red box in c) showing the repeating unit structure of the superlattice in which the constituent Ga, N and Mg atoms are clearly visible. e, A schematic of the superlattice structure from d, detailing the positions of the constituent atoms. f, Atomically resolved EDS spectra across a localized portion of superlattices. Intensity peaks indicate the relative positions of the atomic planes for each element. This region is shown in a HAADF-STEM image (top) in which the arrow marks the line-scanning direction. g, Atomically resolved EDS elemental maps for Ga, N and Mg in the same region as f. Scale bars: 10 nm (a); 2 nm (b); 1 nm (c); 500 pm (f, top); 500 pm (g).