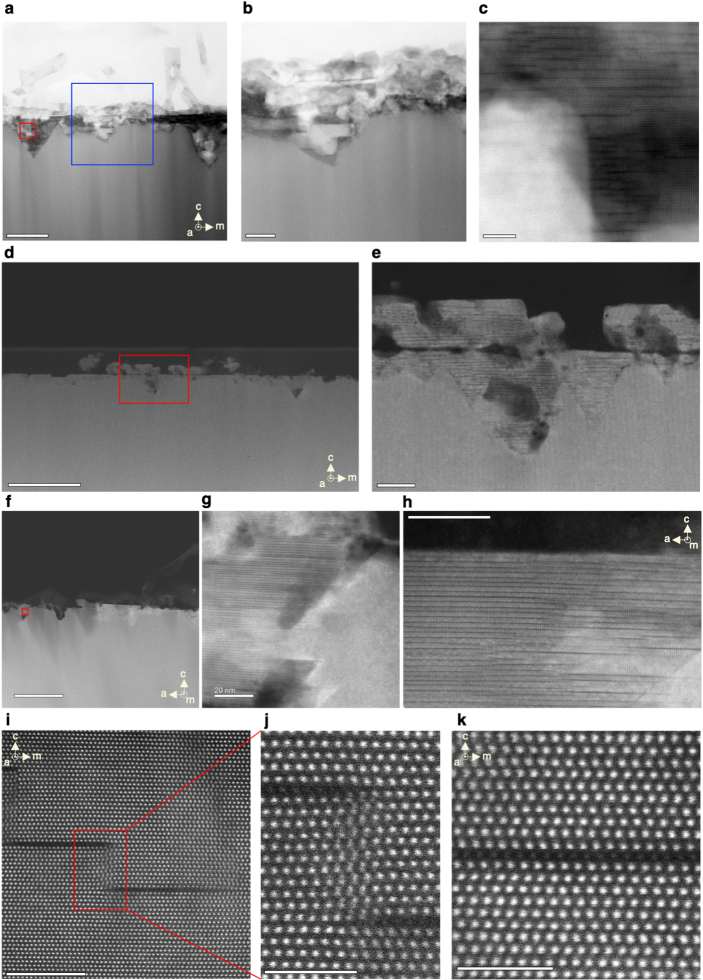
Extended Data Fig. 5. STEM observation of Mg intercalation into GaN.
a, Annular dark field (ADF)-STEM image of Mg-annealed GaN (in default annealing condition of 800 °C for 10 min). Scale bar, 200 nm. b, Magnified view of the area within the blue box in a, revealing the amorphous phase comprising a mixture of Mg and Mg compounds. Scale bar, 50 nm. c, Magnified view of the area within the red box in a. Scale bar: 5 nm. d–f, HAADF-STEM images of the acid-cleaned, Mg-annealed GaN under the same annealing conditions, showing that the amorphous phase can be removed by acid clean. The MiGs phases forming giant inverted pyramids are distinctly visible, along with the observable exfoliation of the MiGs phase at the top, where e is the magnified view of the region within the red box in d. Scale bars: 200 nm, 20 nm, 500 nm, respectively. g, Magnified view of the region in the red box in f. Scale bar: 20 nm. h, HAADF-STEM image showing a detailed MiGs structure. Scale bar: 20 nm. i, Atomically resolved image illustrating two Mg intercalant sheets before vertical alignment, with each sheet approximately 5 nm in size, constrained by the inversion domain region volume. Scale bar, 5 nm. j, A magnified view of the region in the red box in i. Scale bar, 2 nm. k, Atomically resolved HAADF-STEM image along the [] zone axis (a-axis), revealing the Ga atom layer (ABAB ordering) with an inserted single Mg monolayer (C sites), resulting in the ABCAB ordering. Scale bar, 2 nm.