Fig. 6.
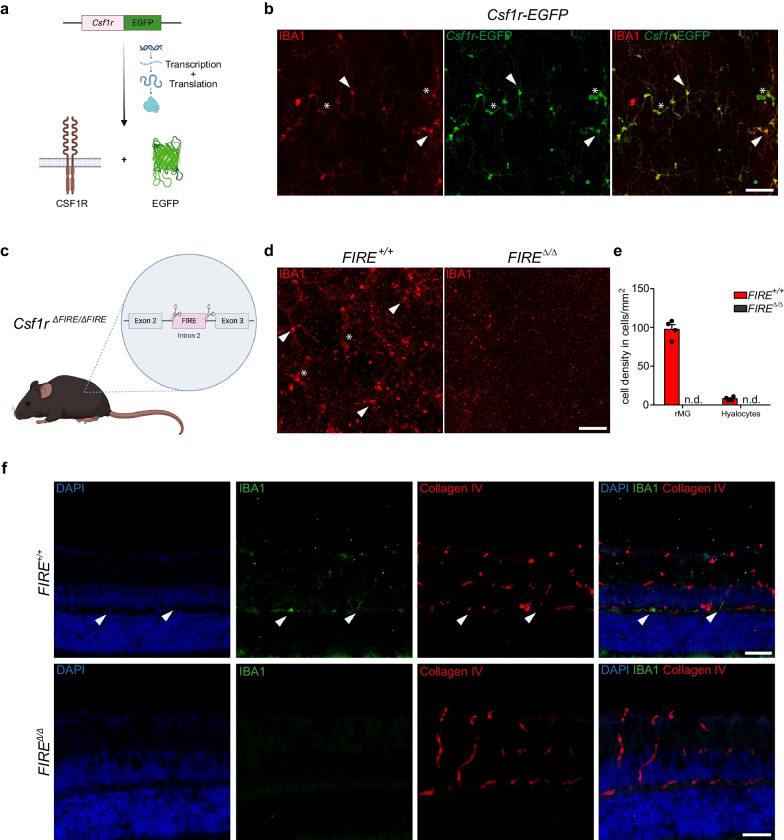
CSF1R-dependence of murine hyalocytes and retinal microglia. a Graphical scheme depicting the experimental setup. In Csf1r-EGFP mice, enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) is expressed under the control of the transgenic Csf1r promoter. Subsequent protein biosynthesis leads to the simultaneous expression of CSF1R and EGFP in these mice. b Confocal images of IBA1 and anti-GFP immunofluorescence co-staining on retinal flat mounts from Csf1r-EGFP mice. EGFP+ hyalocytes (asterisks) and rMG (arrowheads) can be regularly identified. Images are representative for three mice. Scale bar = 50 µm. c Graphical illustration depicting the gene targeting approach in Csf1r∆FIRE/∆FIRE mice. CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing was applied to delete the fms-intronic regulatory element (FIRE) in the second intron of the Csf1r gene locus. d Confocal images of IBA1 immunofluorescence labeling on Csf1r∆FIRE/∆FIRE mice and wildtype controls. Hyalocytes (asterisks) and rMG (arrowheads) can be found in wildtype mice, whereas IBA1+ myeloid cells are completely absent in Csf1r∆FIRE/∆FIRE mice. Images are representative for four mice per group and two independent experiments. Scale bar = 50 µm. e Quantification of microglia and hyalocyte density in Csf1r∆FIRE/∆FIRE (N = 4) and wildtype controls (N = 4). Data are presented as mean S.E.M. f Images from Collagen IV and IBA1 immunofluorescence co-staining on cryo-sections of eyes from wildtype controls (upper panel) and Csf1r∆FIRE/∆FIRE mice (lower panel). Images are representative for four mice per group. Scale bar = 50 µm