Figure 7.
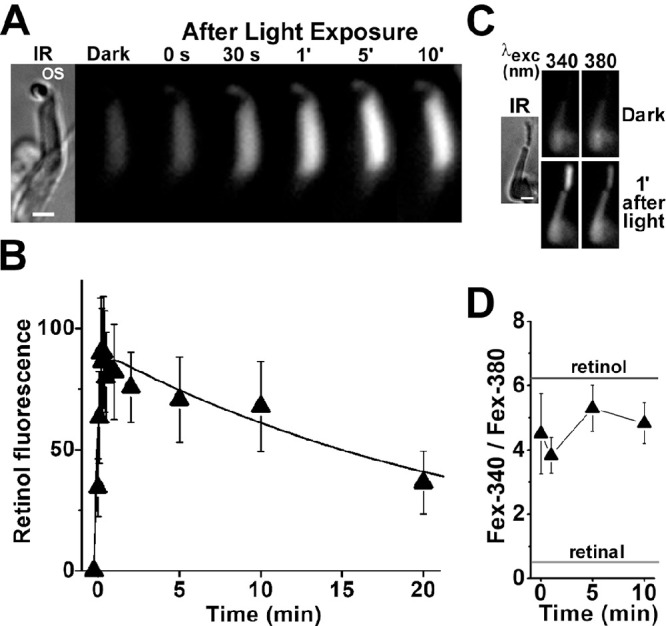
Kinetics of all-trans retinol formation in M. fascicularis cone photoreceptors isolated from dark-adapted eyes. (A) Increase in cone outer segment fluorescence after visual pigment bleaching. IR, infrared image of an isolated M. fascicularis cone photoreceptor; OS denotes the outer segment of the cell. Fluorescence (excitation, 360 nm; emission, >420 nm) images of the cell were acquired before (dark) and at different times after bleaching, which was carried out between t = −0.25 and 0 minute. All fluorescence images are shown at the same intensity scaling. Scale bar: 5 µm. (B) Kinetics of the fluorescence appearing after bleaching of visual pigment in the outer segments of isolated M. fascicularis cone photoreceptors (n = 5). Bleaching was carried out between t = −0.25 and 0 minute. Error bars represent standard errors. All experiments were conducted at 37°C. The solid line is a least-squares fit according to Equation 2, giving a rate constant for the rise in fluorescence of f1 = 4.0 ± 1.1 min–1 and a rate constant for the decline of f2 = 0.04 ± 0.01 min–1. (C) Excitation of outer segment fluorescence with 340-nm and 380-nm light (emission, >420 nm). IR, infrared image of an isolated M. fascicularis cone photoreceptor; fluorescence images of the cell were acquired before (dark) and at 1 minute after the bleaching of visual pigment. Images are shown at the same intensity scaling to facilitate comparisons. Scale bar: 5 µm. (D) Ratio of the intensities of the fluorescence excited by 340-nm (Fex-340) and 380-nm (Fex-380) light in M. fascicularis cone outer segments (n = 10) after visual pigment bleaching. Bleaching was carried out between t = −0.25 and 0 minute. Error bars represent standard errors. The fluorescence intensity ratios determined for all-trans retinal and all-trans retinol (Supplementary Fig. S1) are also shown. All experiments were conducted at 37°C.
