Fig. 3.
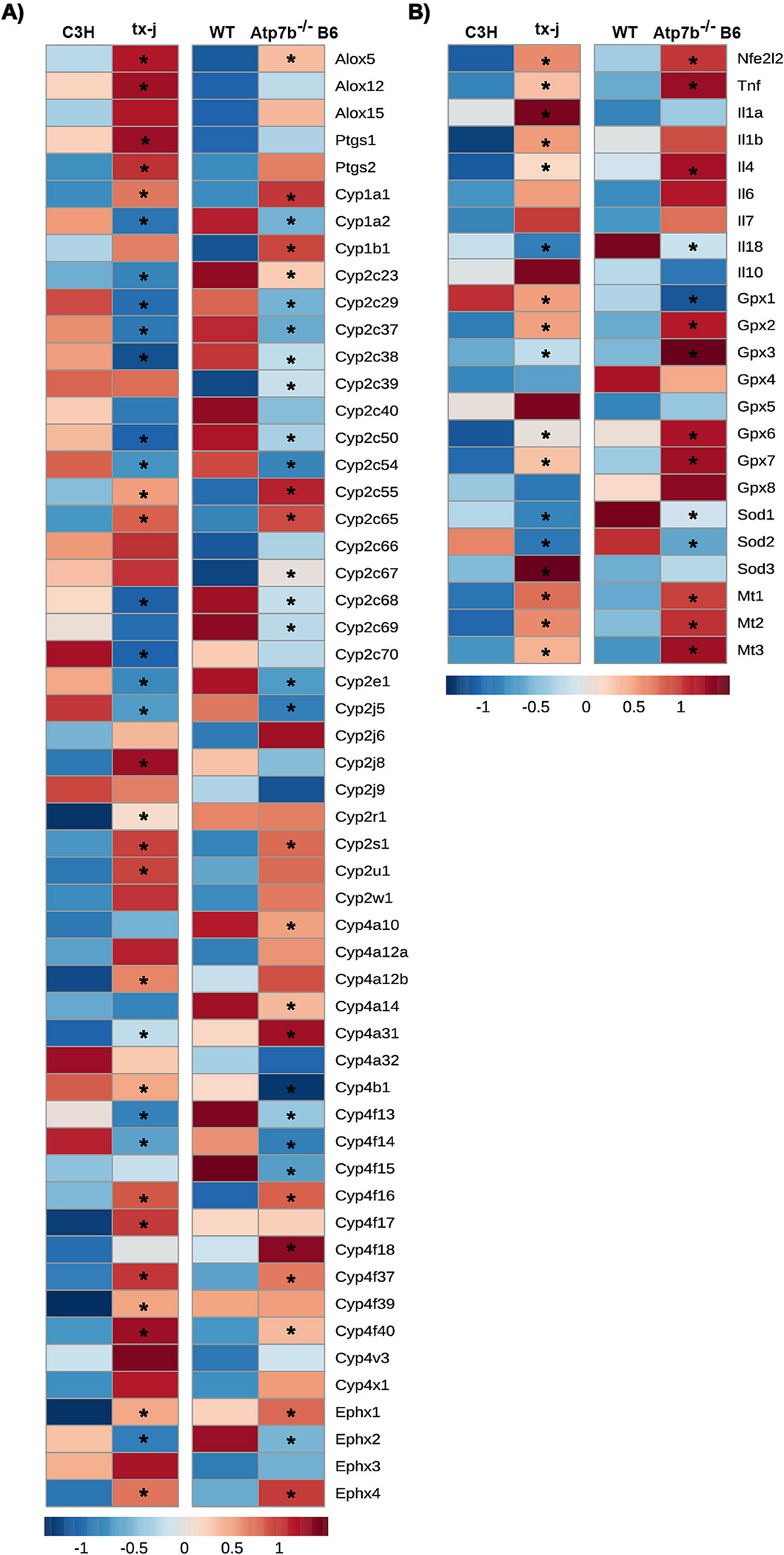
Differences in hepatic gene expression related to PUFA oxidation, oxidative stress and inflammation in two mouse models of Wilson disease compared with controls. Hepatic RNA-seq data of 16-week-old tx-j vs. C3H and Atp7b−/− B6 vs. WT mice illustrating (A) genes related to PUFA enzymatic oxidation, (B) genes related to oxidative stress and inflammation. C3H n = 6 and tx-j n = 6; WT n = 6 and Atp7b−/− B6 n = 6. Data are represented as means ± SEM and statistical significance, (*) indicate P < 0.05. Alox, Arachidonate lipoxygenase gene; Atp7b−/− B6, The Atp7b global knockout on a C57Bl/6 background; C3H, C3HeB/FeJ control mice; Cyp, Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase gene; Gpx, Glutathione peroxidase gene, Il, Interleukin genes; Mt, Metallothionein gene; Nfe2l2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor2 gene; Ptgs, Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase gene; PUFAs, Polyunsaturated fatty acids; Sod, Superoxide dismutase gene; Ephx, Epoxide hydrolases gene; tx-j, The toxic milk mice from The Jackson Laboratory; Tnf, Tumor necrosis factor gene; WD, Wilson disease; WT, Atp7b+/+ controls.
