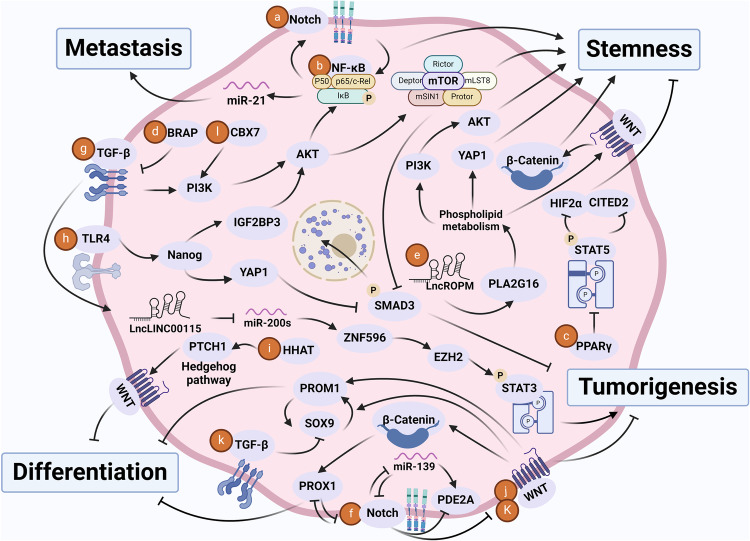
Fig. 4.
Crosstalk of signaling pathways in CSCs. a, b The Notch pathway can be activated by the NF-κB pathway while activating the NF-κB pathway. c PPARγ inhibits the STAT5 pathway to downregulate the expression of HIF2α and CITED2, ultimately attenuating the stemness characteristics of CSCs. d BRAP inhibits the TGF-β/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis to reduce the stemness of CSCs. e LncROPM upregulates PLA2G16 expression to facilitate phospholipid metabolism, which subsequently activates the PI3K/AKT, WNT/β-Catenin, and Hippo/YAP pathways to maintain the stemness of CSCs. f Amplified miR-139 through the miR-139/PDE2A/Notch1 loop, inhibits the WNT pathway to attenuate the tumorigenicity of CSCs. g LINC00115, upregulated by the TGF-β pathway, sponges miR-200s to activate the ZNF596/EZH2/STAT3 axis to promote the stemness and tumorigenesis of CSCs. h Activation of the TLR4/NANOG axis subsequently upregulates the YAP1/SMAD3 and IGF2BP3/AKT/mTOR/SMAD3 pathways to inhibit the nuclear transfer and phosphorylation of SMAD3, ultimately attenuating the tumorigenicity of CSCs. i WNT/β-Catenin pathway downstream effector PROX1 inhibits each other with Notch1, thereby elevating the stemness of CSCs and hindering their differentiation. j PROX1, which can be activated by the WNT/β-catenin pathway, inhibits each other with Notch1, thereby enhancing the stemness of tumor cells and hindering their differentiation. k SOX9/PROM1 positive feedback loop in inhibits differentiation by activating the CSC program, which positively correlates with WNT pathway and negatively correlates with TGF-β pathway. l The PI3K/AKT pathway, activated by CBX7, further stimulating the NF-κB/miR-21 axis, and ultimately promoting the stemness characteristics and metastasis of tumor cells