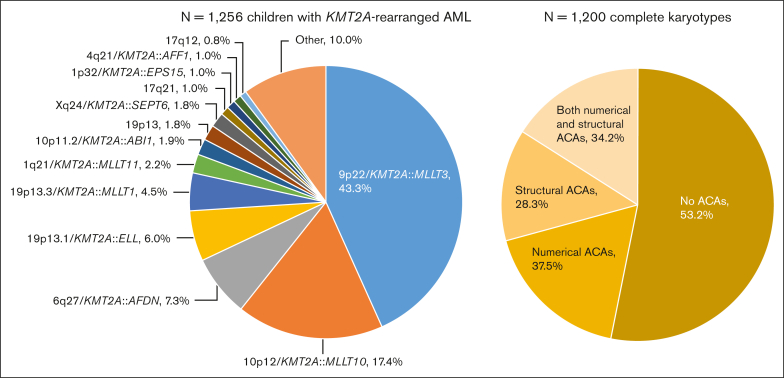
Figure 1.
Distribution of the fusion-based groups and the presence and type of ACAs in our cohort of childhood KMT2A-r AML. 9p22/KMT2A::MLLT3 refers to t(9;11)(p22;q23) (n = 544), 10p12/KMT2A::MLLT10 to t(10;11)(p12;q23) (n = 218), 6q27/KMT2A::AFDN to t(6;11)(q27;q23) (n = 92), 19p13.1/KMT2A::ELL to t(11;19)(q23;p13.1) (n = 75), 19p13.3/KMT2A::MLLT1 to t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) (n = 56), 1q21/KMT2A::MLLT11 to t(1;11)(q21;q23) (n = 28), 10p11.2/KMT2A::ABI1 to t(10;11)(p11.2;q23) (n = 24), 19p13 to t(11;19)(q23;p13) without ascertained subband (n = 23), Xq24/KMT2A::SEPT6 to t(X;11)(q24;q23) (n = 22), 17q21 to t(11;17)(q23;q21) (n = 13), 1p32/KMT2A::EPS15 to t(1;11)(p32;q23) (n = 13), 4q21/KMT2A::AFF1 to t(4;11)(q21;q23) (n = 12), and 17q12 to t(11;17)(q23;q12) (n = 10). Of the 1200 patients with complete karyotypes, 638 had no ACAs and 562 had ACAs, of whom 211 had solely numerical ACAs, 159 solely structural aberrations, and 192 both numerical and structural ACAs. Figure created with BioRender.com.