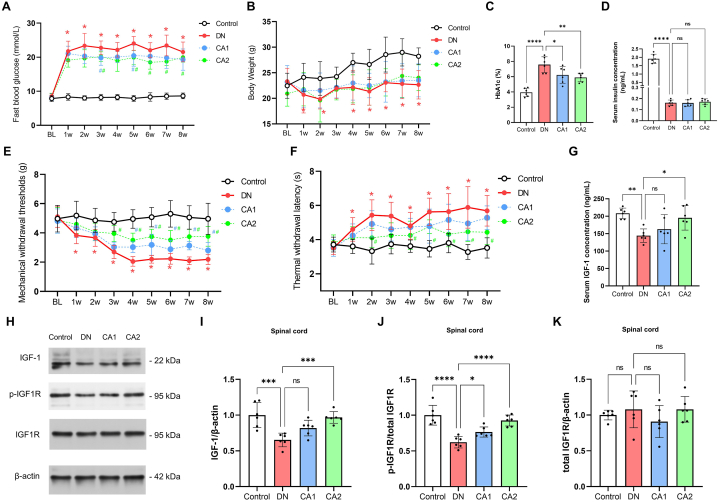
Fig. 2.
Caffeic acid mitigates diabetic neuropathy (DN) and revives spinal IGF-1 signaling. (A) Longitudinal alterations in fasting blood glucose levels at Baseline (BL, immediately prior to STZ injection), and at weekly intervals for 8 weeks following STZ injection. Red asterisks (*) denote P < 0.05 when comparing DN group to control group at specified time points. Blue or green hashtags (#) represent P < 0.05 when comparing CA1 or CA2 groups, respectively, to the DN group at those time points. Statistical significance was determined using a multiple comparison test following a two-way ANOVA. (B) Time-course changes in body weight from BL for 8 weeks after STZ injection. Notations as explained in (A). (C) Comparative examination of blood HbA1c percentage among four experimental groups, 8 weeks after STZ administration. (D) Comparison of serum insulin levels among four experimental groups, 8 weeks after STZ administration. (E) Longitudinal variations in mechanical withdrawal thresholds from BL for 8 weeks following STZ injection. Notations as explained in (A). (F) Time-course changes in thermal withdrawal latency from BL for 8 weeks post-STZ injection. Notations as explained in (A). (G) Examination of serum IGF-1 concentration, 8 weeks after STZ administration. (H–K) Comparative assessment of spinal protein levels of IGF-1, phosphorylated IGF1R (p-IGF1R), and total IGF1R, 8 weeks post-STZ injection. Statistical significance is denoted as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, while 'ns' denotes non-significant findings.