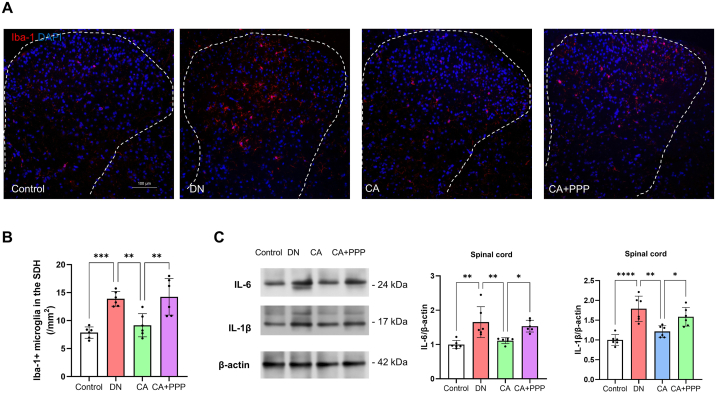
Fig. 7.
The anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid in the spinal cord of DN mice are mitigated by the co-administration of PPP. (A) Depictions of Iba-1 immunostaining (red) in the SDH of the control, DN, CA, and CA + PPP groups, 8 weeks after STZ injection. DAPI (blue) counterstaining was employed to highlight nuclei. Scale bars correspond to 100 μm. (B) Quantitative evaluation of Iba-1+ microglial cells in the SDH. (C) Comparative analysis of spinal protein levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β among the control, DN, CA, and CA + PPP groups, 8 weeks following STZ injection. Levels of statistical significance are designated as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, while 'ns' signifies non-significant outcomes.