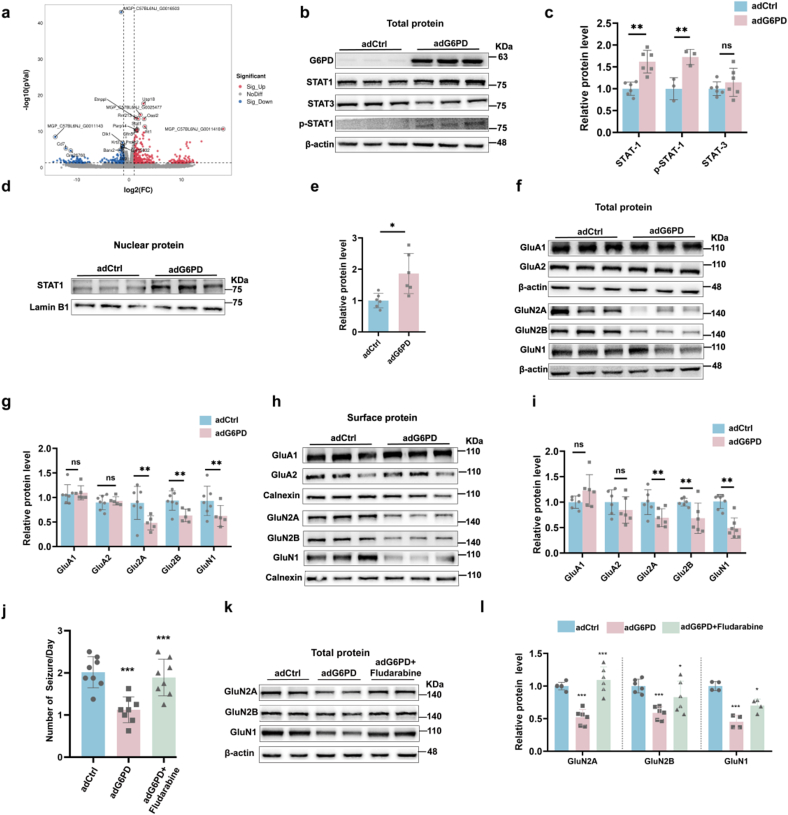
Fig. 4.
G6PD negatively regulates the expression of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptors (NMDARs) through increasing STAT1 (a) RNA sequencing revealed that G6PD increased the transcription of Stat1 in epileptic mice. (b–e) Representative immunoblots (b, d) and quantification (c, e) of total STAT1 (n = 6), STAT3 (n = 6), p-STAT1 (n = 3), and nuclear STAT1 (n = 6) expression in the hippocampi of mice from the adCtrl and adG6PD groups. (f–i) Representative immunoblots (f, h) and quantification (g, i) of total and surface protein expression of NMDARs in the mouse hippocampus from the adCtrl and adG6PD groups (n = 6). Data are presented as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. (j) Effect of G6PD overexpression on the number of daily spontaneous recurrent seizures in the adCtrl, adG6PD, and adG6PD + fludarabine groups (n = 8). Data are presented as means ± SEM. ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. (k–l) Representative immunoblots (b) and quantification (c) of NMDARs (Glu2A, Glu2B, and GluN1) in the hippocampi of mice in the adCtrl, adG6PD, and adG6PD + fludarabine groups (n = 6). Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test.