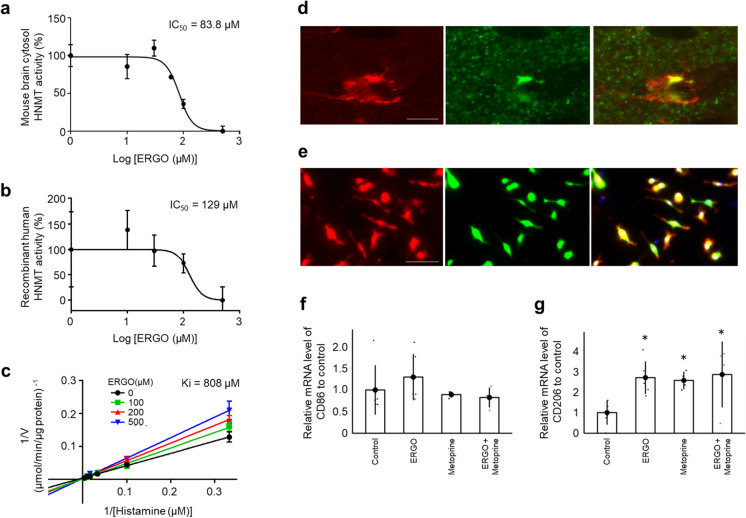
Fig. 6.
ERGO inhibited the histamine-metabolizing enzyme and promoted polarization of anti-inflammatory M2 microglia. a Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of ERGO (0, 10, 30, 60, 100, and 500 µM) on histamine metabolism in mouse brain cytosol (20 µg/mL) and b the effect of ERGO (0, 10, 30, 100, and 500 µM) on rhHNMT (10 nM). c Lineweaver–Burk plots on the data of the inhibition of rhHNMT by ERGO. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). d Immunohistochemical detection of HNMT (green) and the microglial marker Iba1 (red) in mouse hippocampus. Scale bar, 5 µm. e Immunocytochemical detection of HNMT (green) and Iba1 (red) in mouse PMG. Scale bar, 50 µm. f qRT–PCR determination of the relative levels of the M1 microglial marker CD86 and g M2 microglial marker CD206 mRNA in mouse PMG. Data are the mean ratio ± SEM of transcript levels normalized to gapdh (n = 4–6). *P < 0.05 versus control (Dunnett’s test). PMG, primary cultured microglia; rhHNMT, recombinant human histamine N-methyltransferase; qRT–PCR, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction