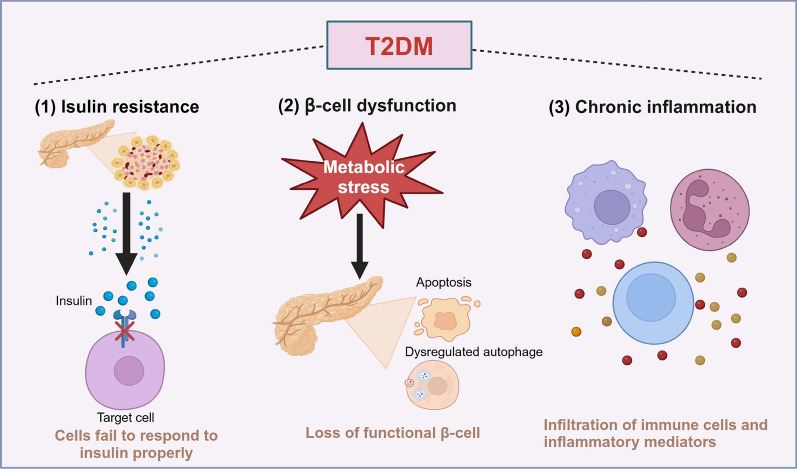
Fig. 4.
Pathophysiological mechanisms of T2DM. Insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction and chronic inflammation are the three main pathophysiological changes in T2DM. (1) In T2DM, although insulin is released by pancreas islet β cell, the target cells can not respond to insulin; (2) Metabolic stress leads to the apoptosis and dysregulated autophagy of β cells, contributing to the reduced functional β cells; (3) The increased infiltration of immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, results in the increased levels of inflammatory mediators