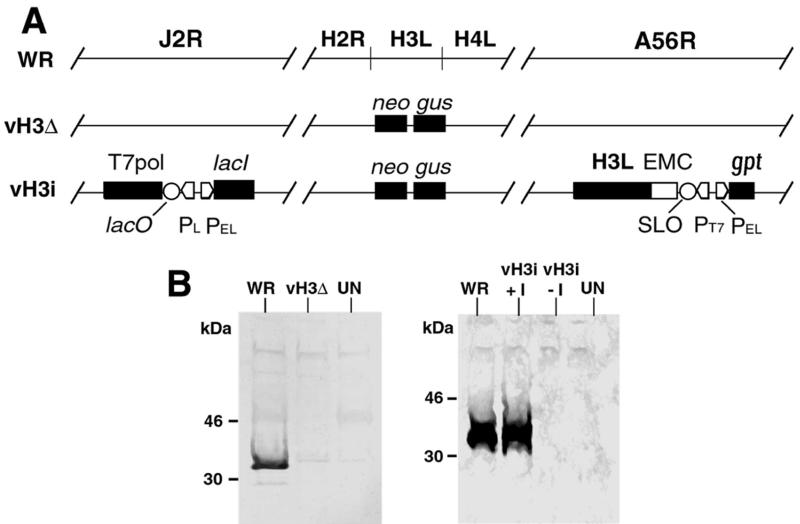
FIG. 1.
Representation of wild-type and mutant genomes. (A) Genomes of wild-type and recombinant viruses. Shown are genome segments containing the following ORFs: J2R (encoding thymidine kinase) H2R, H3L, H4L, and A56R (encoding hemagglutinin). In vH3Δ, the H3L ORF is replaced by the neo and gus genes, which are regulated by vaccinia virus promoters and which provide antibiotic selection and positive identification of plaques. In vH3i, (i) the H3L ORF is replaced by the neo and gus genes regulated by vaccinia virus promoters, (ii) the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase ORF regulated by the E. coli lac operator (lacO) and the vaccinia virus P11 late promoter (PL) and the E. coli lac repressor (lacI) regulated by the vaccinia virus P7.5 early/late promoter (PEL) are inserted into the J2R ORF, and (iii) the H3L ORF preceded by the encephalomyocarditis virus untranslated leader sequence (EMC) providing cap-independent translation, a modified lacO (SLO), and a bacteriophage T7 promoter (PT7) as well as the E. coli gpt gene regulated by a vaccinia virus promoter for antibiotic selection are inserted into the A56R ORF. (B) Expression of the H3L ORF. BS-C-1 cells that were uninfected (UN) or infected with WR, vH3Δ, or vH3i in the presence (+I) or absence (−I) of IPTG were harvested after 24 h and the lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antiserum to a peptide encoded by the H3L ORF. The H3L protein was detected by chemiluminescence. The positions and masses of marker proteins are indicated at the left.