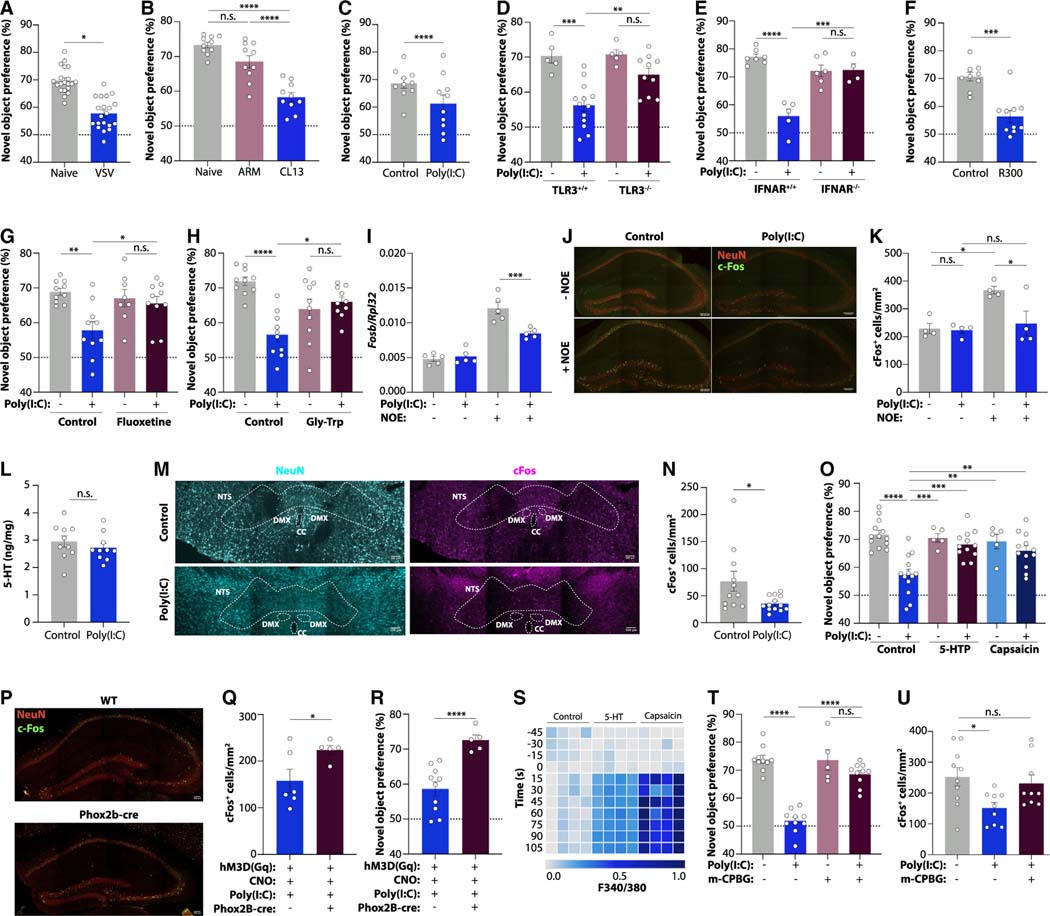
Figure 7. Serotonin deficiency drives cognitive dysfunction via vagal signaling.
(A–H) Novel object preference in mice infected with VSV (A) or LCMV ARM or CL13 at day 14 post-infection (B); poly(I:C)-treated wild-type (C), TLR3−/− (D), and IFNAR−/− mice (E); platelet-depleted mice (F); poly(I:C)-treated mice receiving the SSRI fluoxetine (G); and poly(I:C)-treated mice fed a Gly-Trp dipeptide diet (H).
(I) Fosb expression in the hippocampus of poly(I:C)-treated mice with or without novel object exposure (NOE).
(J and K) Representative images (J) and quantification (K) of cFos+ cells in the dentate gyrus of poly(I:C)-treated mice with or without NOE. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(L) Serotonin concentrations in the brains of poly(I:C)-treated mice.
(M and N) Representative images (M) and quantification (N) of cFos+ cells in the nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) of poly(I:C)-treated mice. Scale bars, 100 μm. Outlined are NTS, dorsal motor nucleus (DMX), and central canal (CC).
(O) Novel object preference in mice receiving poly(I:C), 5-HTP, or capsaicin.
(P–R) Representative images (P) and quantification of cFos+ cells in the dentate gyrus following NOE (Q) and novel object preference (R) of Phox2b-cre mice injected with AAV-hM3Dq, CNO, and poly(I:C). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(S) Calcium signaling of cultured vagal neurons exposed to capsaicin or serotonin.
(T and U) Novel object preference (T) and quantification of cFos+ cells in the dentate gyrus (U) of mice treated with poly(I:C) and the 5-HT3 receptor agonist m-CPBG.
Plotted are means ± SEM. n.s. p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. See also Figure S7.