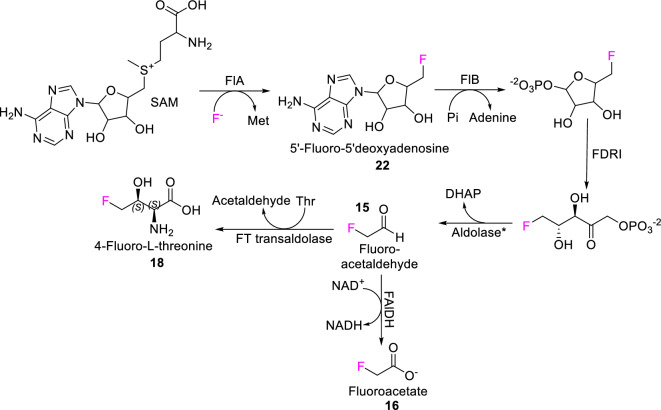
Figure 3.
Biosynthesis of C–F bonds. The first native fluorinase that has been characterized is a nucleophilic halogenase, flA from Streptomyces cattleya. The fluorinase flA, isolated from S. cattleya in 200272, catalyses C–F bond formation from an inorganic fluoride ion. FlA fluorinase mediates a reaction between S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) and a fluoride ion to yield 5’-fluorodeoxyadenosine (22) and L-methionine, the first step in the biosynthesis of fluoroacetate (16) and 4-fluorothreonine (18). SAM S-adenosyl-L-methionine, Met L-methionine, Pi phosphate, DHAP dihydroxyacetone phosphate, NADH/NAD+: reduced and oxidized variants of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, FlA: Fluorinase, FlB 5′-fluoro-5′-deoxyadenosine phosphorylase, FDRI 5-fluoro-5-deoxyribose-1-phosphate isomerase, FAlDH fluoroacetaldehyde dehydrogenase, FT transaldolase fluorothreonine transaldolase. *putative aldolase responsible for the formation of fluoroacetalaldehyde (15). Figure modified and adapted from37.